Research Highlights
-
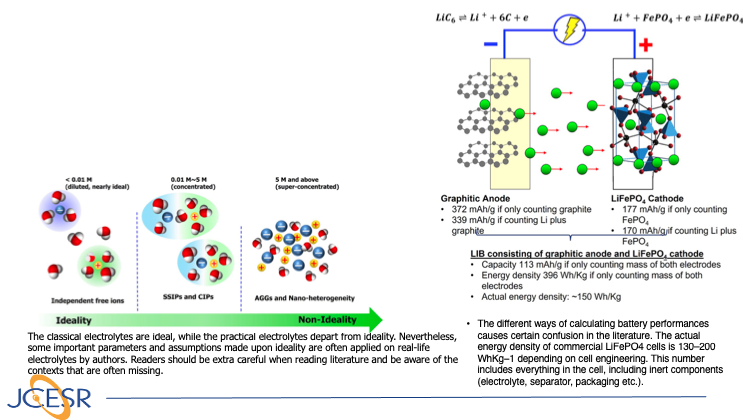
Navigating the Minefield of Battery Literature
This is an invited perspective aiming to help researchers new to the field of battery research to circumvent certain recurring misconceptions and inaccuracies in the current battery literature. It covers the electrolyte ideality and practical situation in batteries, the difficulty in accurately determining ion transference… Read More
-
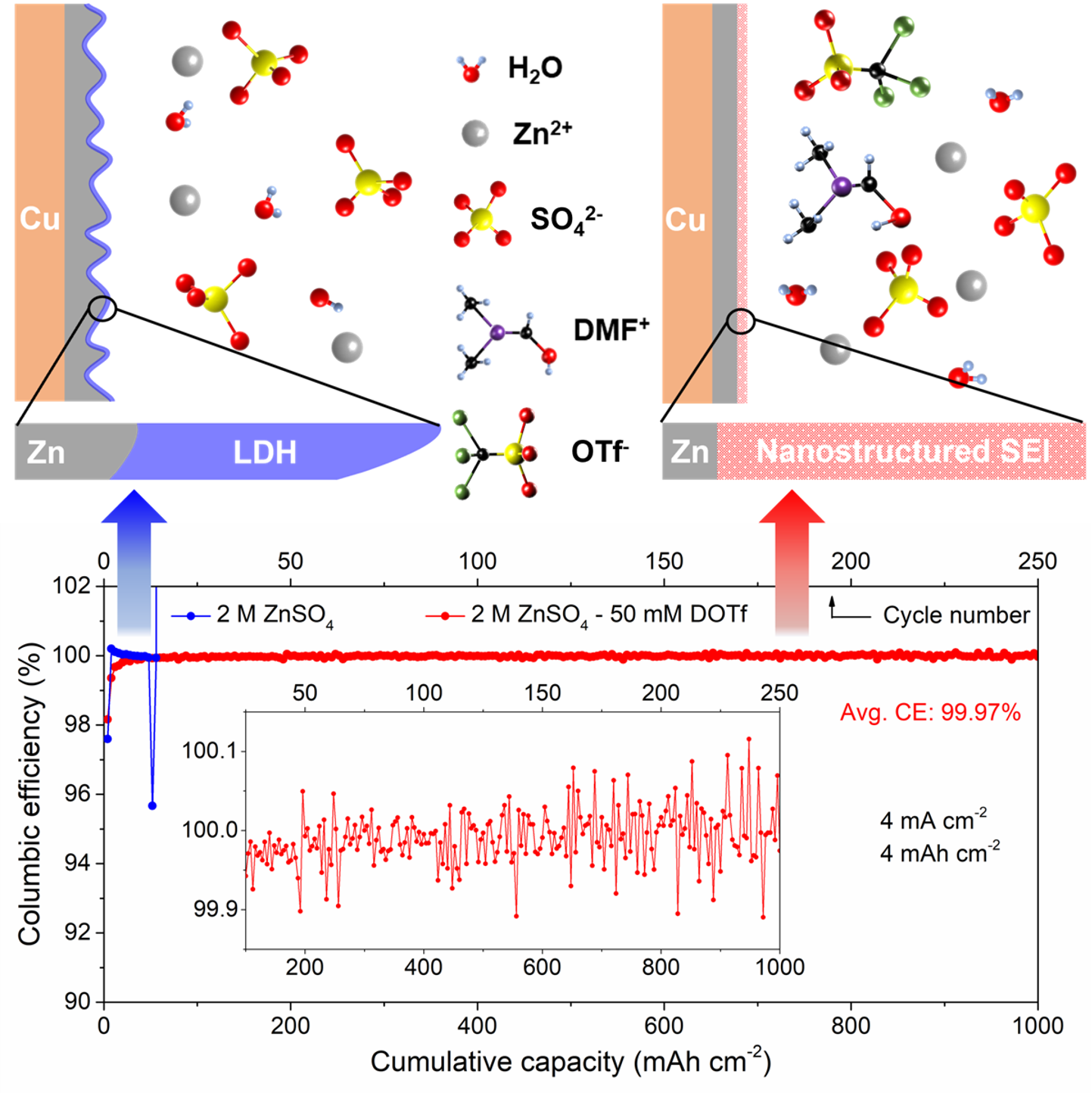
Highly reversible Zn anode with a practical areal capacity enabled by a sustainable electrolyte and superacid interfacial chemistry
We introduced - N,N-dimethylformamidium trifluoromethanesulfonate (DOTf) - as a novel low-concentration electrolyte additive for aqueous Zn metal batteries. This electrolyte leads to dendrite-free and highly reversible Zn plating/stripping with close-to-100% average CE at practical cycling conditions (current density of 4 mA cm-2 and areal capacity of 4 mAh cm-2) with long cycle life. Read More
-
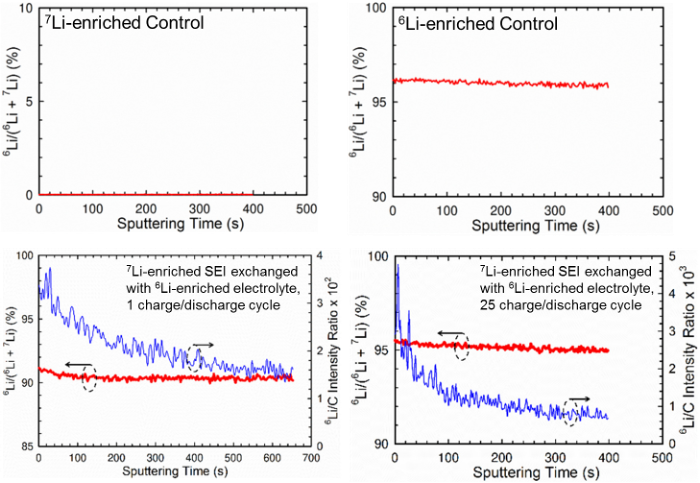
Quantifying Lithium Ion Exchange in Solid Electrolyte Interphase (SEI) on Graphite Anode Surfaces
By using Li isotopic labelling of SEIs and electrolytes followed by time-of-flight secondary-ion mass spectroscopy and solid-state NMR analyses, we found that the majority of Li+ “immobilized” in the chemical ingredients were exchanged after 1 SEI formation cycle. Ion exchange by diffusion based on concentration gradient without applied potential also occurred simultaneously. Read More
-
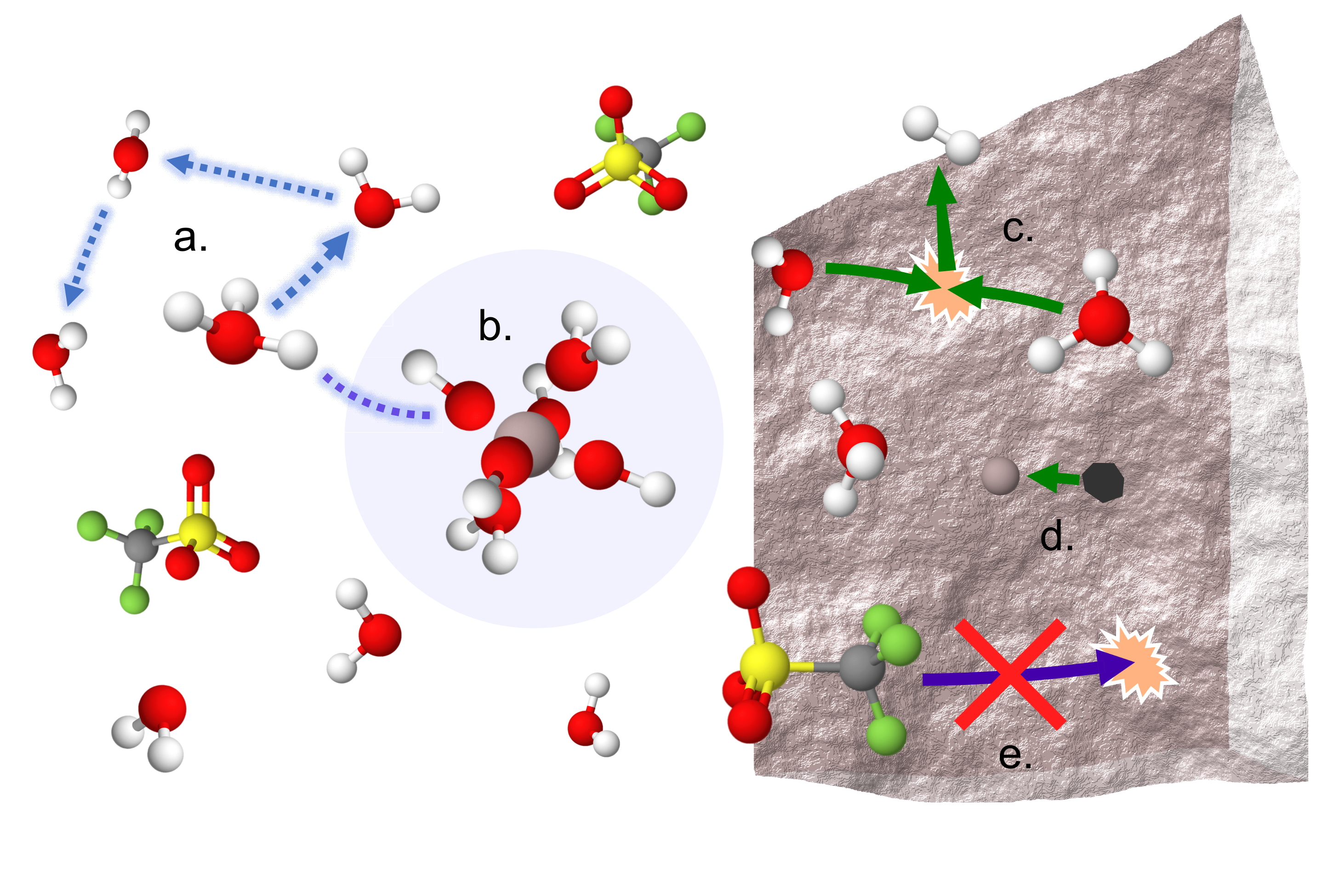
A Sobering Examination of the Feasibility of Aqueous Aluminum Batteries
We revealed the first compelling evidence for a dynamic octahedral solvation structure around Al3+ dominated by labile water and OH-, without Al-OTf contact ion pairs, at high salt concentrations. High proton activity is observed in transport and electrochemical measurements which relates well with the proposed solvation environment. Read More
-
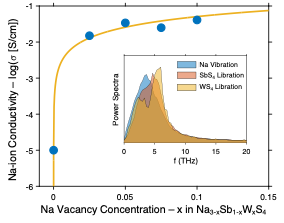
Ion Migration Mechanisms in the Sodium Sulfide Solid Electrolyte Na3-xSb1-xWxS4
The atomic-scale mechanisms that underlie the exceptionally high ionic conductivity of Na3-xSb1-xWxS4 are elucidated. The conductivity is well explained by a combination of vacancy-related effects and a strong overlap of cation vibrational modes with anion librations. Read More
-
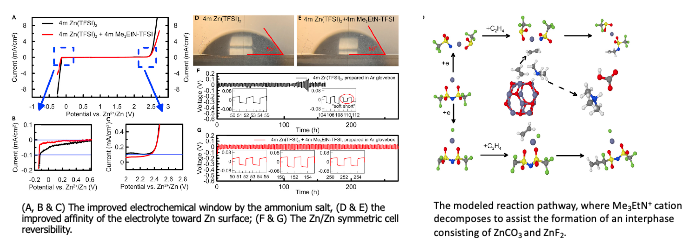
Ammonium enables reversible aqueous Zn battery chemistries by tailoring the interphase
As a continued effort to make Zn metal anode reversible at lower cost, researchers at ARL explored a new supporting salt based on ammonium salt to alter the interfacial structure and interphasial chemistries. The salt was synthesized at ARL and much cheaper than the phosphonium… Read More
-
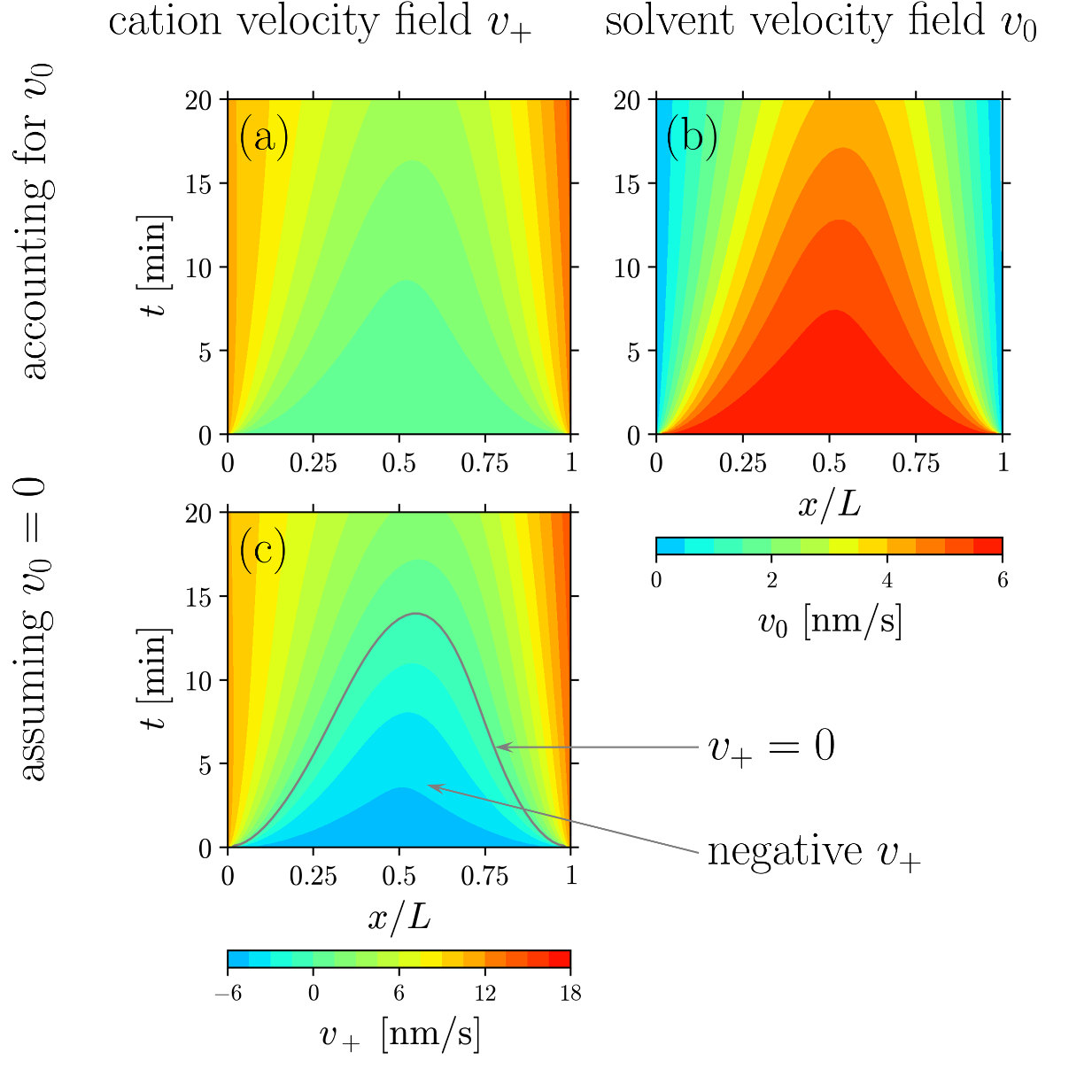
Effect of Solvent Motion on Ion Transport in Electrolytes
Typically, the solvent is assumed to be immobile in a polarized electrolyte. However, recent JCESR measurements show non-zero solvent velocity. This article proposes a continuum theory to predict such solvent motion and its influence on other electrolyte fields. Read More
-
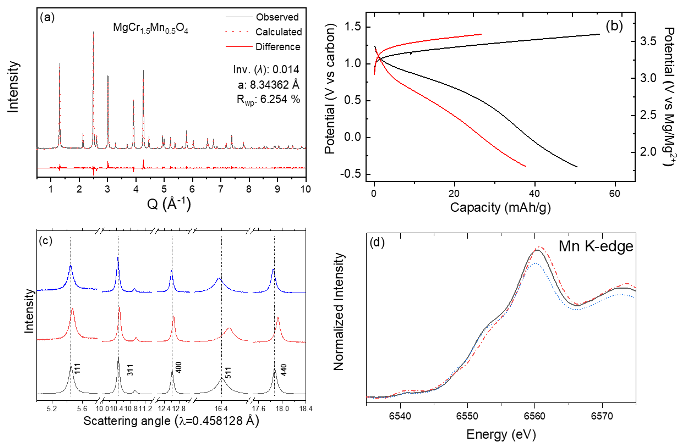
Facile Electrochemical Mg-Ion Transport in a Defect-Free Spinel Oxide
Inversion-free spinel MgCr1.5Mn0.5O4 was successfully synthesized. The tailored spinel showed reversible (de)intercalation of Mg2+ at high redox potentials. It was found that the overpotentials and, thus, overall hysteresis was reduced when the inversion ratio in the spinel lattice was minimized. The experimental evidence emphasizes the influence of structural defects, in this case inversion, on electrochemical Mg2+ activity and provides a design rule toward a building functional Mg cathode for a high-energy Mg-ion battery. Read More
-
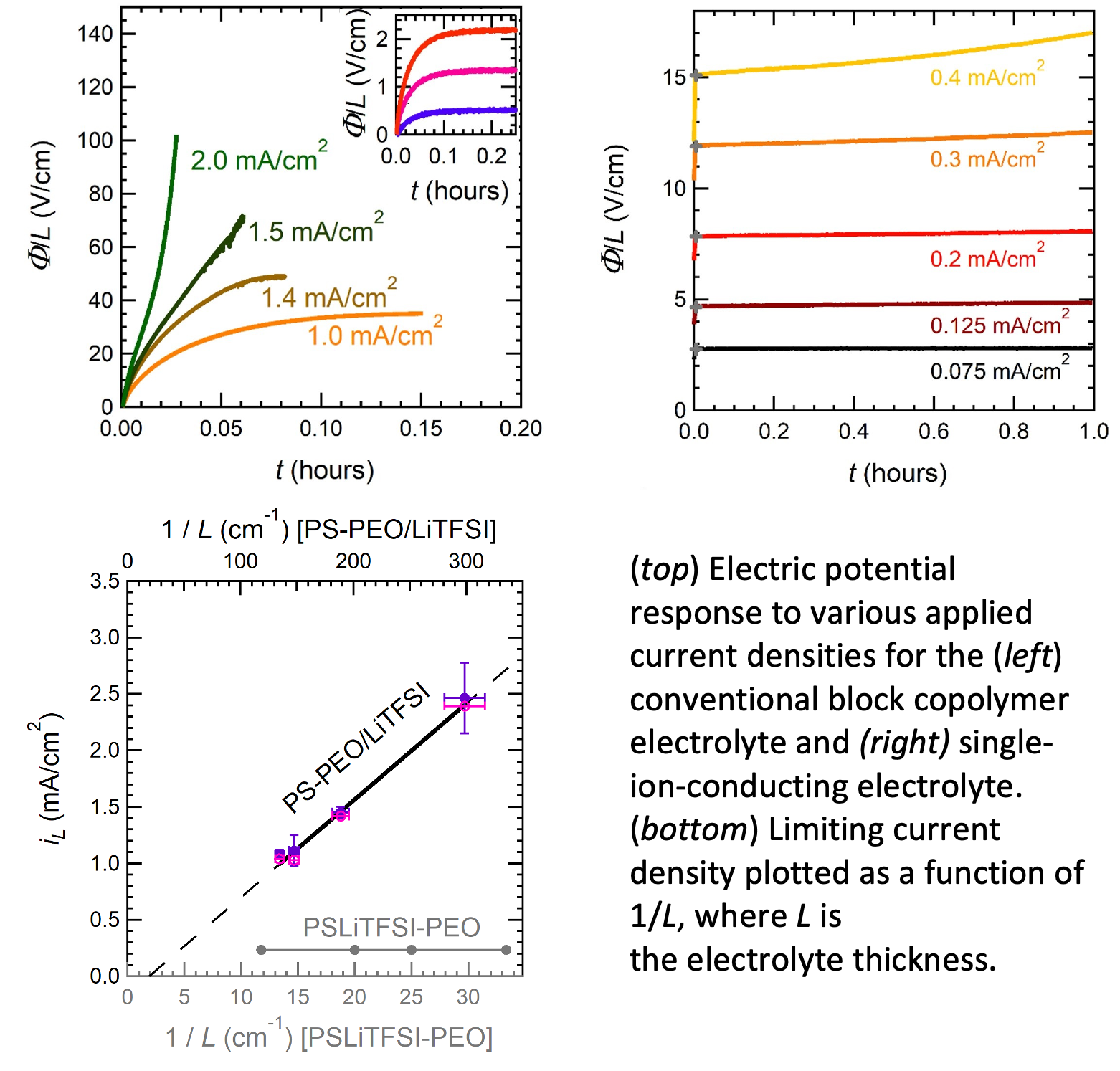
Limiting Current in Single-Ion-Conducting and Conventional Block Copolymer Electrolytes
The performance of an electrolyte in a battery is determined by the limiting current – the maximum allowable current before detrimental irreversible side-reactions take over. We have developed a methodology for determining limiting current in electrolytes with mobile cations and anions (conventional liquid electrolytes) and electrolytes with only one mobile ion (single-ion conductors such as inorganic ceramics and glasses). Read More
-
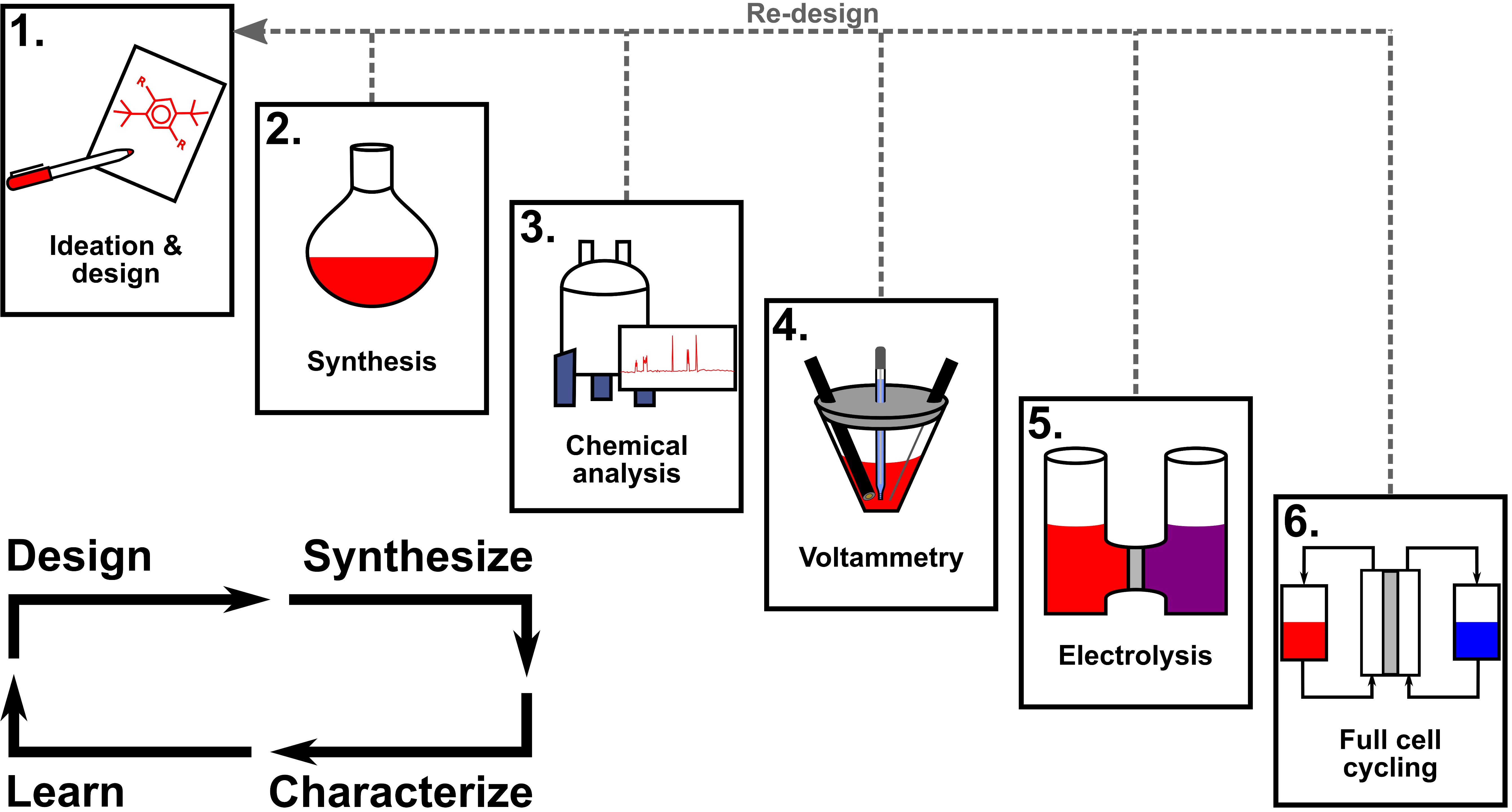
From the synthesis vial to the full cell: Electrochemical methods for characterizing active materials for redox flow batteries
We describe foundational electrochemical methods in the context of redox flow batteries, discussing proper experimental methodology, data interpretation, and limitations for evaluating key properties that translate to device performance. Read More
Latest Updates
-
You’re Invited - JCESR and Beyond: Translating the Basic Science of Batteries
Please join us at Argonne National Laboratory on Tuesday, April 4, 2023 for JCESR and Beyond: Translating the Basic Science of Batteries. Registration is now open. This in-person event will celebrate 10 years of research from the Joint Center… Read More
-
A Message from JCESR: In Memory of George Crabtree
It is with heavy hearts that we say goodbye to George Crabtree, a Senior Scientist and Distinguished Fellow at Argonne National Laboratory, and Director of the Joint Center for Energy Storage Research (JCESR), who passed away unexpectedly on January 23. Dr. Read More
-
Cyanopyridines As Extremely Low-Reduction-Potential Anolytes for Nonaqueous Redox Flow Batteries
Discovery of a cyanophenylpyridine derivative with a very low reduction potential and good stability during cycling. Read More
-
Characterizing Redoxmer – Electrode Kinetics Using a SECM-Based Spot Analysis Method
Identified asymmetries in electron transfer (ET) kinetics between the reduction and oxidation of ferrocene-based redoxmers by measuring the ET rate constants (kf/kb) as a function of electrode potential. Read More
-
Benzotriazoles as Low Potential Anolytes for Non-Aqueous Redox Flow Batteries
We developed an easy-to-synthesize benzotriazole-based anolyte with a high energy redox potential (-2.3 V vs Fc/Fc+) and high solubility that demonstrates stable electrochemical cycling performance. Read More

