Scientific Achievement
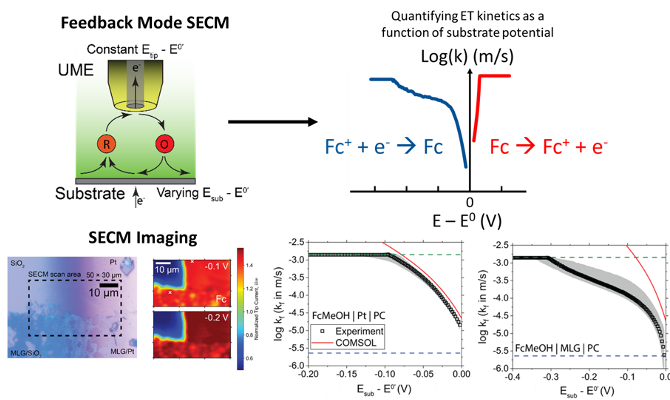
Identified asymmetries in electron transfer (ET) kinetics between the reduction and oxidation of ferrocene-based redoxmers by measuring the ET rate constants (kf/kb) as a function of electrode potential.
Significance and Impact
An SECM protocol was developed to electrochemically characterize the electrode-electrolyte interfaces. Our work revealed a unique interplay between the solvent, electrolyte, and carbon electrode that results in slower ET during the reduction of Fc+ but enhancement during the oxidation of Fc.
Research Details
- Reliable quantification of Butler – Volmer (B-V) kinetic parameters such as kf and α. As well as discern deviations from idealities
- Lower rate constants were measured for the reduction of Fc+ consistently over a wide range carbon electrodes in PC solvent. However, no such impeded kinetics observed during the oxidation of Fc
- Investigated ET behavior of interfaces at high redoxmer concentrations, which is not possible via conventional electrochemical techniques

