Research Highlights
-
Li+ hopping mechanism in LiTFSI water-in-salt electrolyte identified by molecular dynamics simulations
The high Li+ apparent transference number in the LiTFSI water-in-salt electrolyte was captured by MD simulations and the dominant Li+ conduction mechanism in the highly concentrated LiTFSI water-in-salt electrolyte was identified to be hopping between water and TFSI- anions. Read More
-
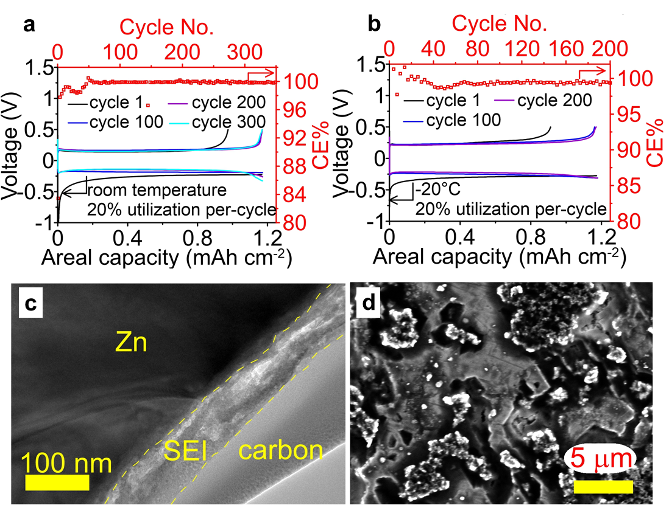
High-Efficiency Zinc-Metal Anode Enabled by Liquefied Gas Electrolytes
A liquefied gas electrolyte was developed for the 1st time for a bivalent chemistry. It displays an excellent Zn conductivity (>3.4 mS cm-1) across a broad temperature range (-60 to +20 °C), enables highly reversible Zn cycling with no evidence of shorting behavior at both room temperature and -20 °C for over 200 cycles (>400 h) with a high Coulombic efficiency (CE > 99%) at high utilization (20% Zn per cycle) for Zn plating/stripping at both room temperature and -20°C. Read More
-

Limited Accessibility to Surface Area Generated by Thermal Pretreatment of Electrodes Reduces Its Impact on Redox Flow Battery Performance
A systematic study on thermally pretreated electrodes for redox flow batteries (RFBs) leveraging gas adsorption techniques, physicochemical spectroscopy, in situ flow cells, and a convection-reaction model suggests diminishing returns in RFB performance at longer pretreatment times due to hindered active species transport to recessed regions of the electrode. Read More
-
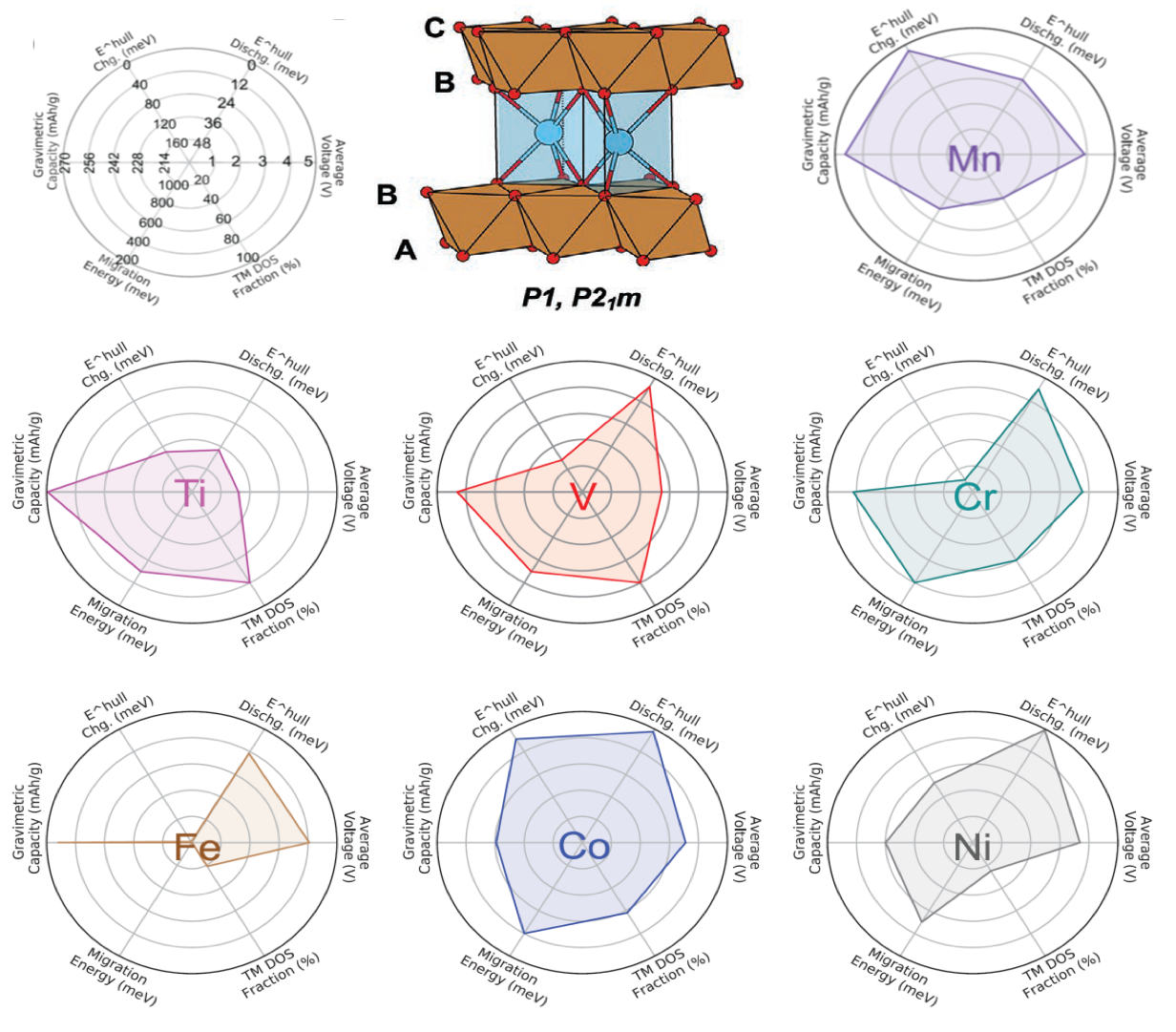
First-principles calculations predict Ca cathodes based on layered calcium transition metal oxide materials
First-principles calculations are used to demonstrate that P-type layered CaTM2O4 materials with a range of TM substitutions (TM = Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, and Ni) have excellent battery-related properties including thermodynamic stability, average voltage, energy density, synthesizability, ionic mobility, and electronic structure. Read More
-

Understanding Solvation Behavior of the Saturated Electrolytes with Small/Wide-Angle X-ray Scattering and Raman Spectroscopy
A combined SAXS/WAXS and Raman spectroscopy are employed to study the global and local solvation structure. This work demonstrates a method for detecting the structure of liquids, which will facilitate the study of structure-performance relationships and the screening of new electrolytes. Read More
-
Pulsed Field Gradient Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Diffusion Analysis in Battery Research (Review)
A pedagogical overview of Pulsed Field Gradient Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (PFG-NMR) analysis for battery electrolytes provides a guide for new and seasoned practitioners, while demonstrating the many uses of diffusion measurements through a review of selected examples. Read More
-
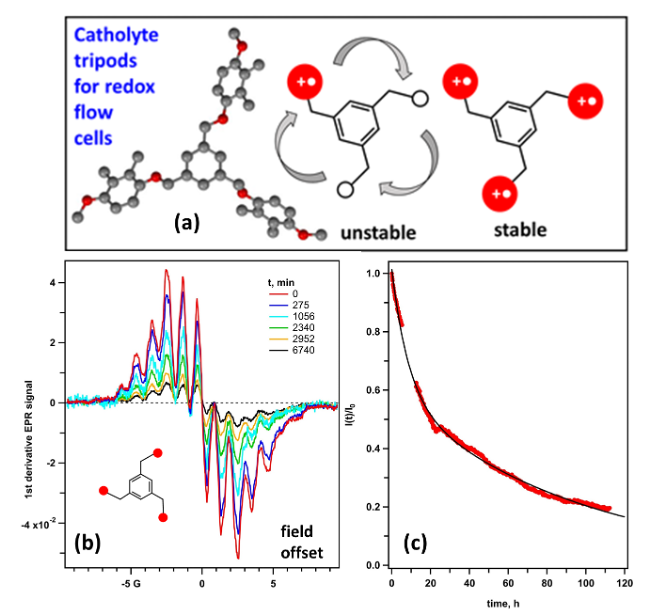
Multiple charging of tripodal catholyte redoxmers
Redox-active oligomer molecules can become more (100x) stable when they are fully charged compared to their partially charged states. This is the first time this effect was observed in chemistry. Read More
-
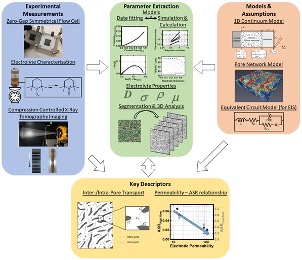
Combining electrochemical and imaging analyses to understand the effect of electrode microstructure and electrolyte properties on redox flow batteries
Through a combined experimental and modeling approach, we show that, of the many physical properties associated with fibrous electrodes, permeability best correlates with electrochemical performance in a flow cell. Read More
-
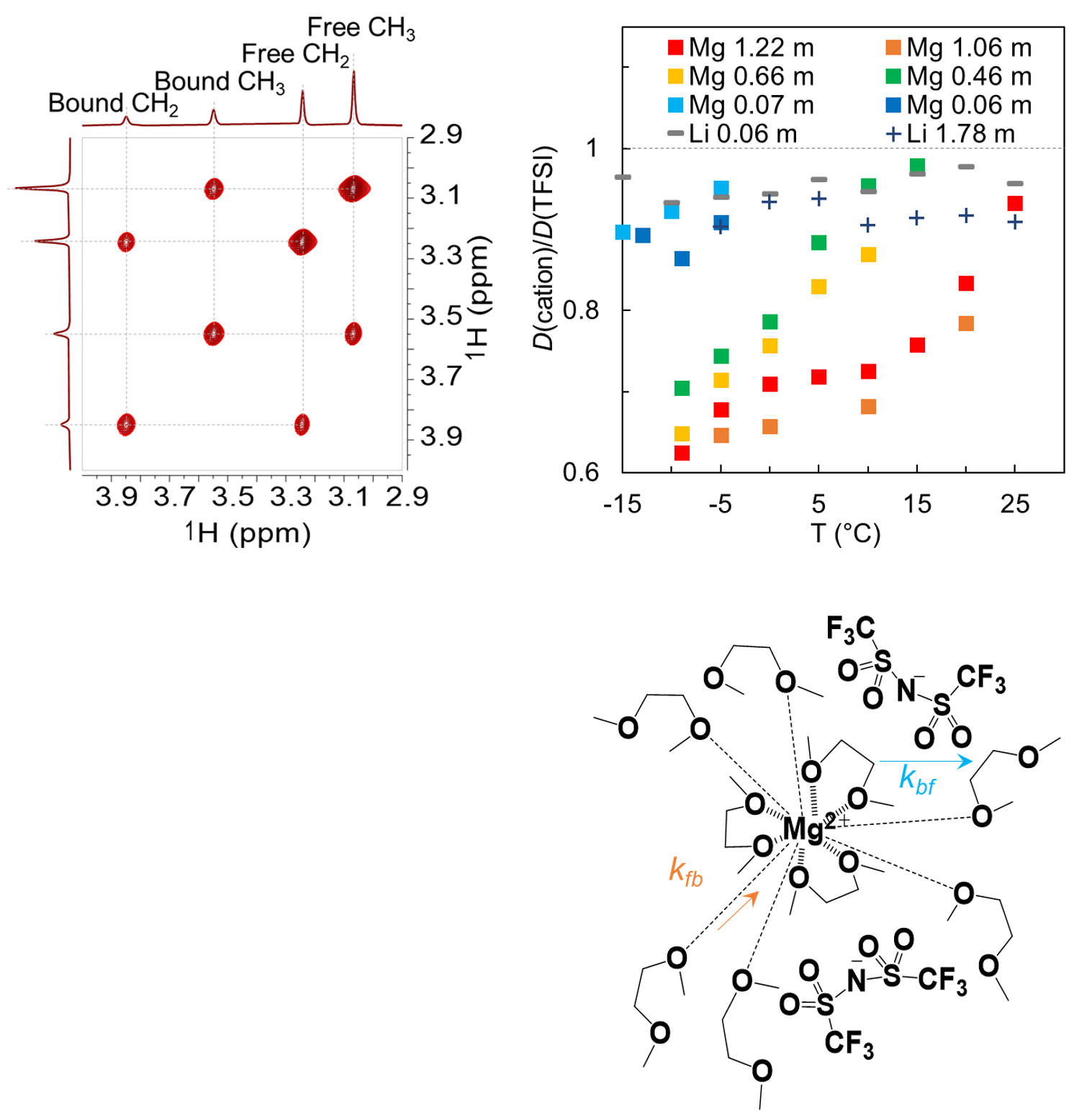
Role of Multivalent Ion – Solvent Interaction on Restricted Mg2+ Diffusion in Dimethoxyethane (DME) Electrolytes
Comparison of the diffusion behaviors of Mg2+, TFSI-, DME, and Li+ reveals a relative restriction to Mg2+ diffusion that is caused by the long-range interaction between Mg2+ and solvent molecules, especially those with suppressed motions at high concentrations and low temperatures. Read More
-
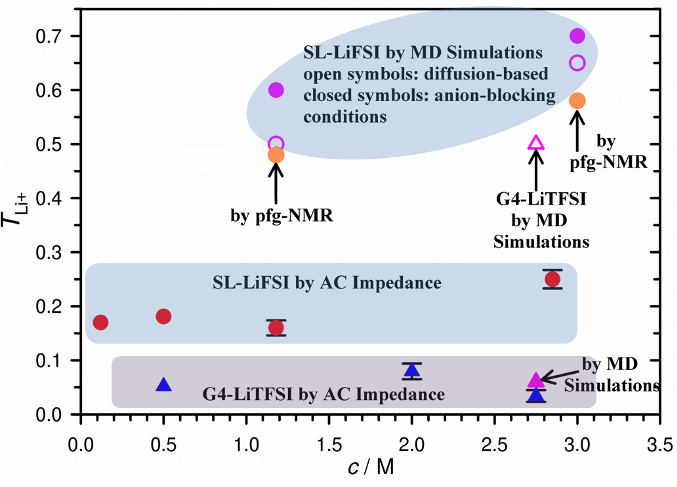
Tabc Li+ in Sulfolane-and Tetraglyme-based Electrolytes by Very Low Frequency Impedance Spectroscopy (VLF-IS)
A systematic study of the effect of concentration on Li+ transference number under anion-blocking conditions (_(〖〗^+)^) in sulfolane (SL) and tetraglyme (G4) using VLF-IS showed that SL is a more superior solvent than G4 for Li+ transport, even though the viscosity of the former is higher but with similar ionic conductivity. Read More
Latest Updates
-
You’re Invited - JCESR and Beyond: Translating the Basic Science of Batteries
Please join us at Argonne National Laboratory on Tuesday, April 4, 2023 for JCESR and Beyond: Translating the Basic Science of Batteries. Registration is now open. This in-person event will celebrate 10 years of research from the Joint Center… Read More
-
A Message from JCESR: In Memory of George Crabtree
It is with heavy hearts that we say goodbye to George Crabtree, a Senior Scientist and Distinguished Fellow at Argonne National Laboratory, and Director of the Joint Center for Energy Storage Research (JCESR), who passed away unexpectedly on January 23. Dr. Read More
-
Cyanopyridines As Extremely Low-Reduction-Potential Anolytes for Nonaqueous Redox Flow Batteries
Discovery of a cyanophenylpyridine derivative with a very low reduction potential and good stability during cycling. Read More
-
Characterizing Redoxmer – Electrode Kinetics Using a SECM-Based Spot Analysis Method
Identified asymmetries in electron transfer (ET) kinetics between the reduction and oxidation of ferrocene-based redoxmers by measuring the ET rate constants (kf/kb) as a function of electrode potential. Read More
-
Benzotriazoles as Low Potential Anolytes for Non-Aqueous Redox Flow Batteries
We developed an easy-to-synthesize benzotriazole-based anolyte with a high energy redox potential (-2.3 V vs Fc/Fc+) and high solubility that demonstrates stable electrochemical cycling performance. Read More

