Research Highlights
-
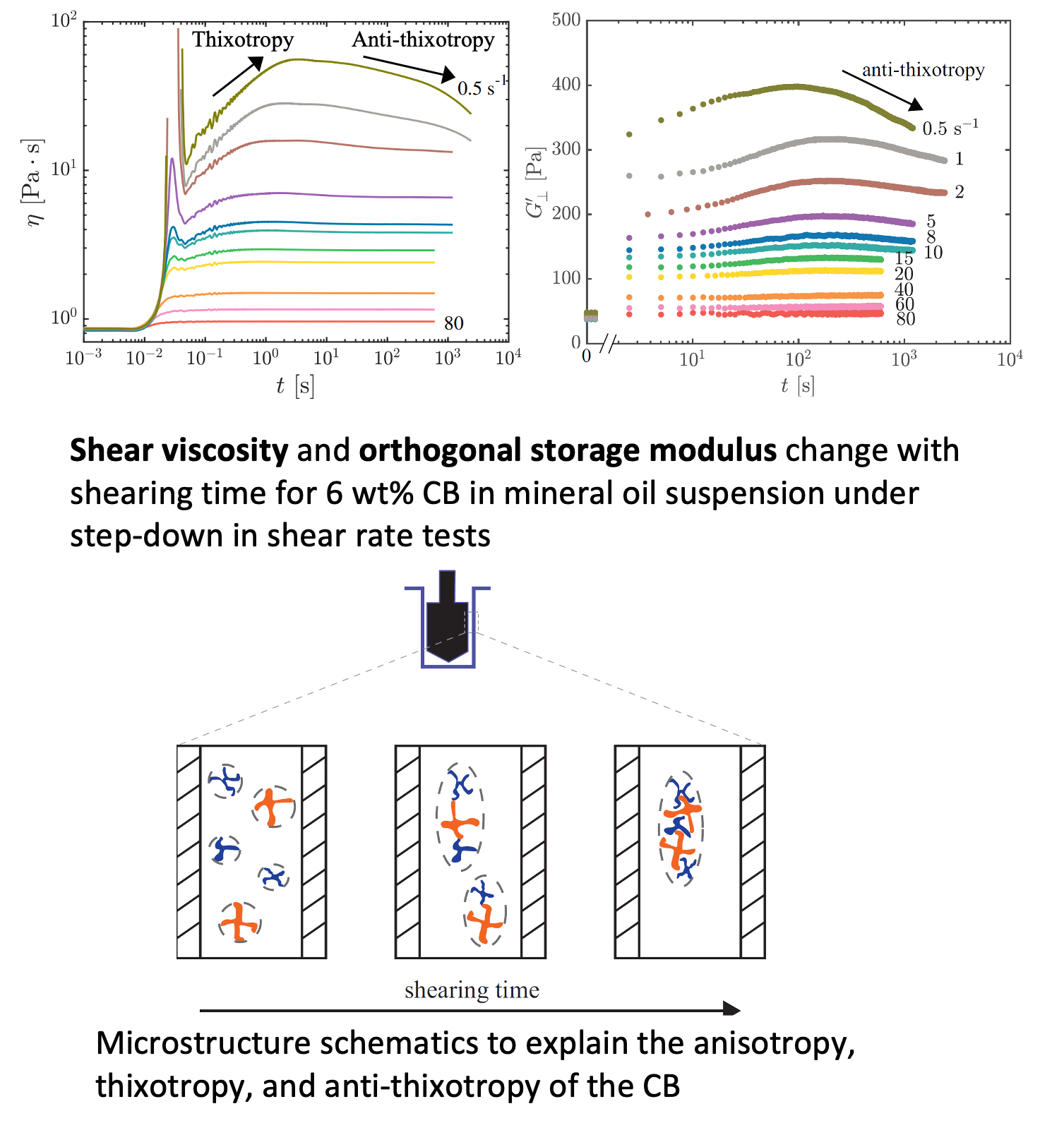
Rheology of suspension of carbon black (CB) – a conductive additive in flow batteries
Carbon black (CB), a conductive additive used in flow batteries, is proved to show thixotropy (less flowable with time under step-down in shear rate) and anti-thixotropy (more flowable with time), and this is rationalized with a qualitative mechanical model. Read More
-
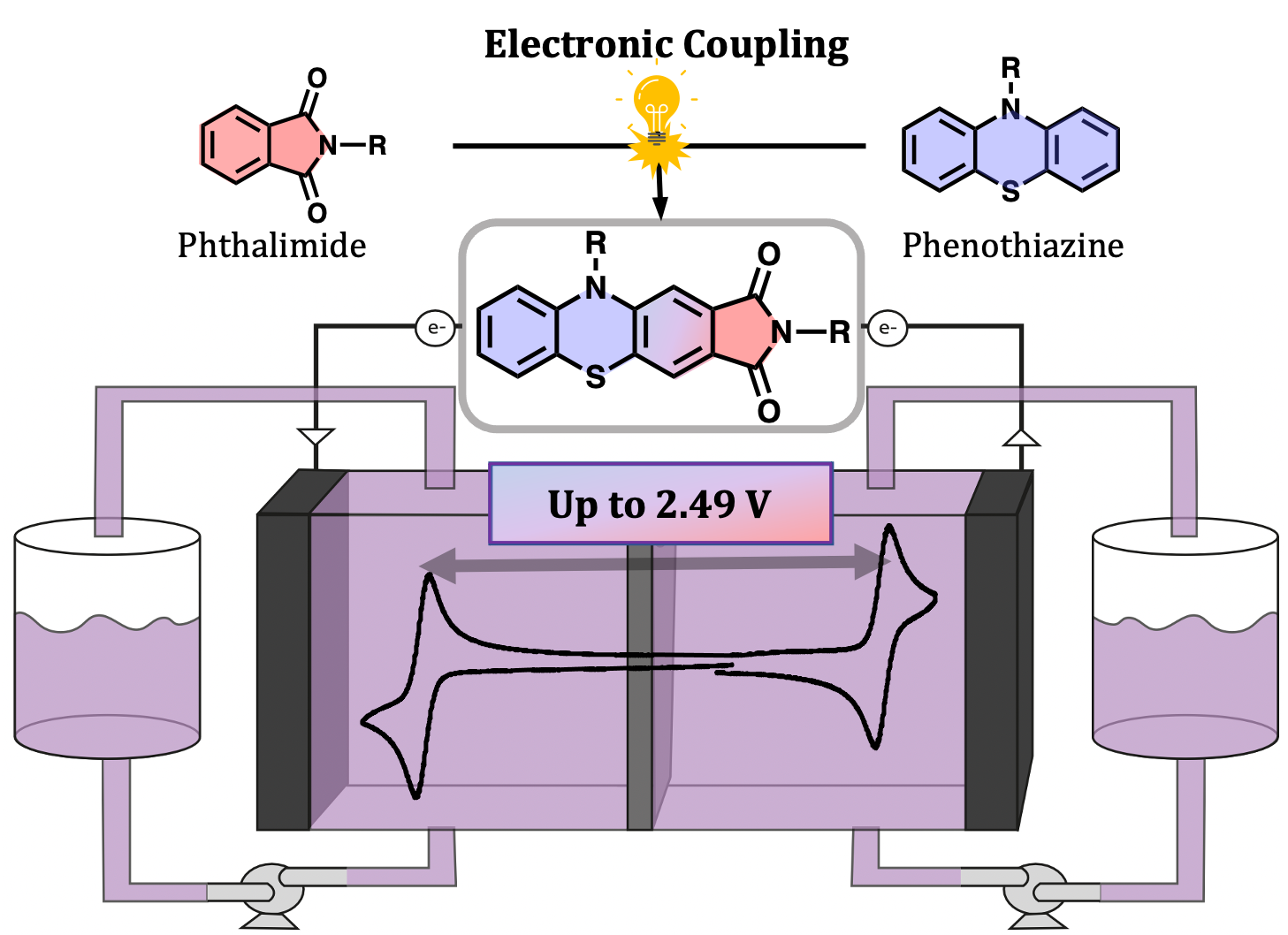
Improving Flow Battery Voltages by Electronically Coupling Anolyte and Catholyte Structures
Phenothiazine catholytes and phthalimide anolytes have been electronically coupled to create a new class of bipolar redox-active molecules (i.e. molecules that can be both reversibly oxidized and reduced) with enhanced voltages as compared to what can be achieved by their uncoupled building blocks. Read More
-
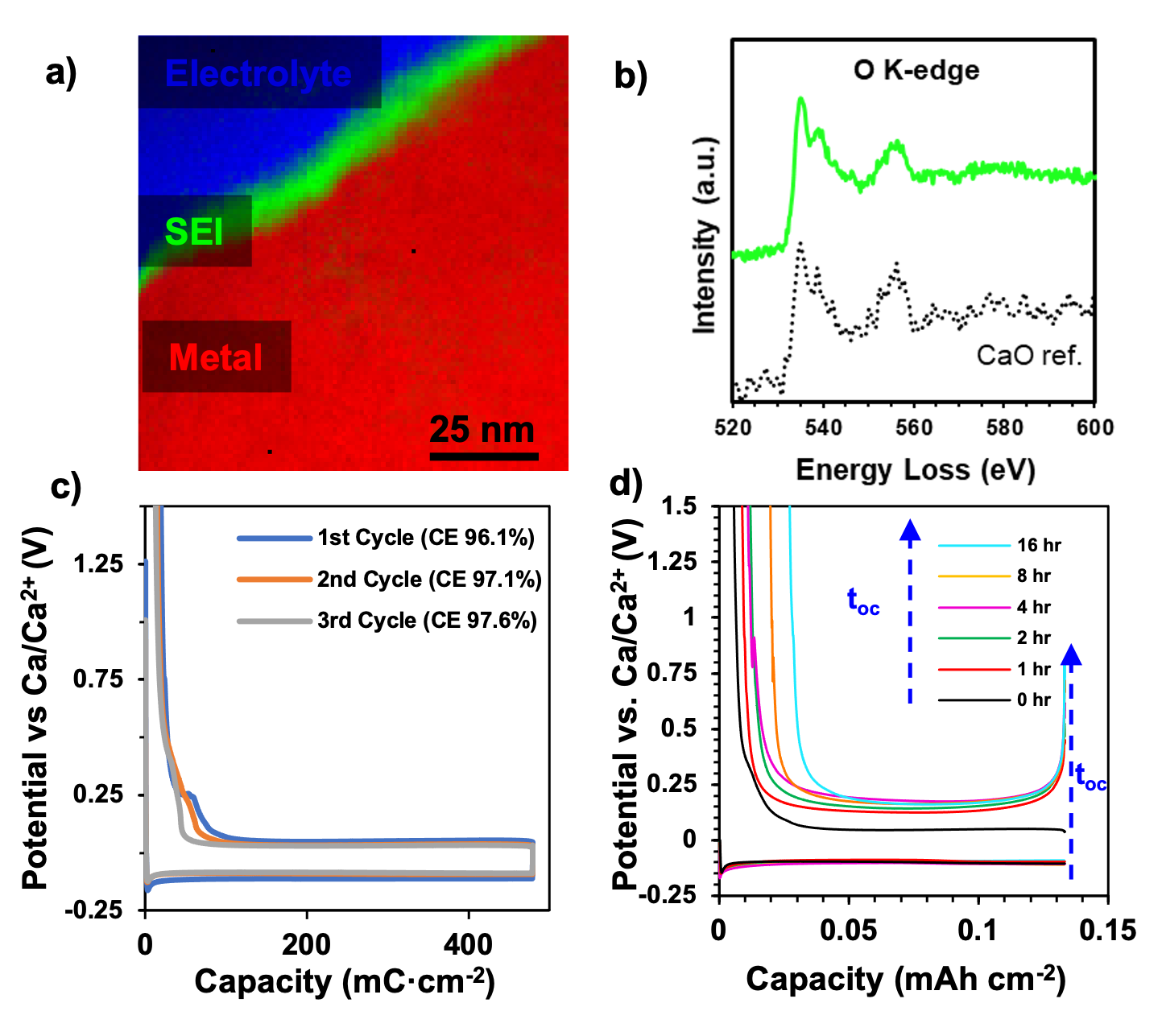
A Heterogeneous Oxide Enables Reversible Calcium Electrodeposition for a Calcium Battery
The solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) formed on the calcium anode during reversible calcium electrodeposition has been compositionally mapped revealing the role of a heterogenous, nanometric calcium oxide as the responsible cation conductor and protective interphase. Read More
-
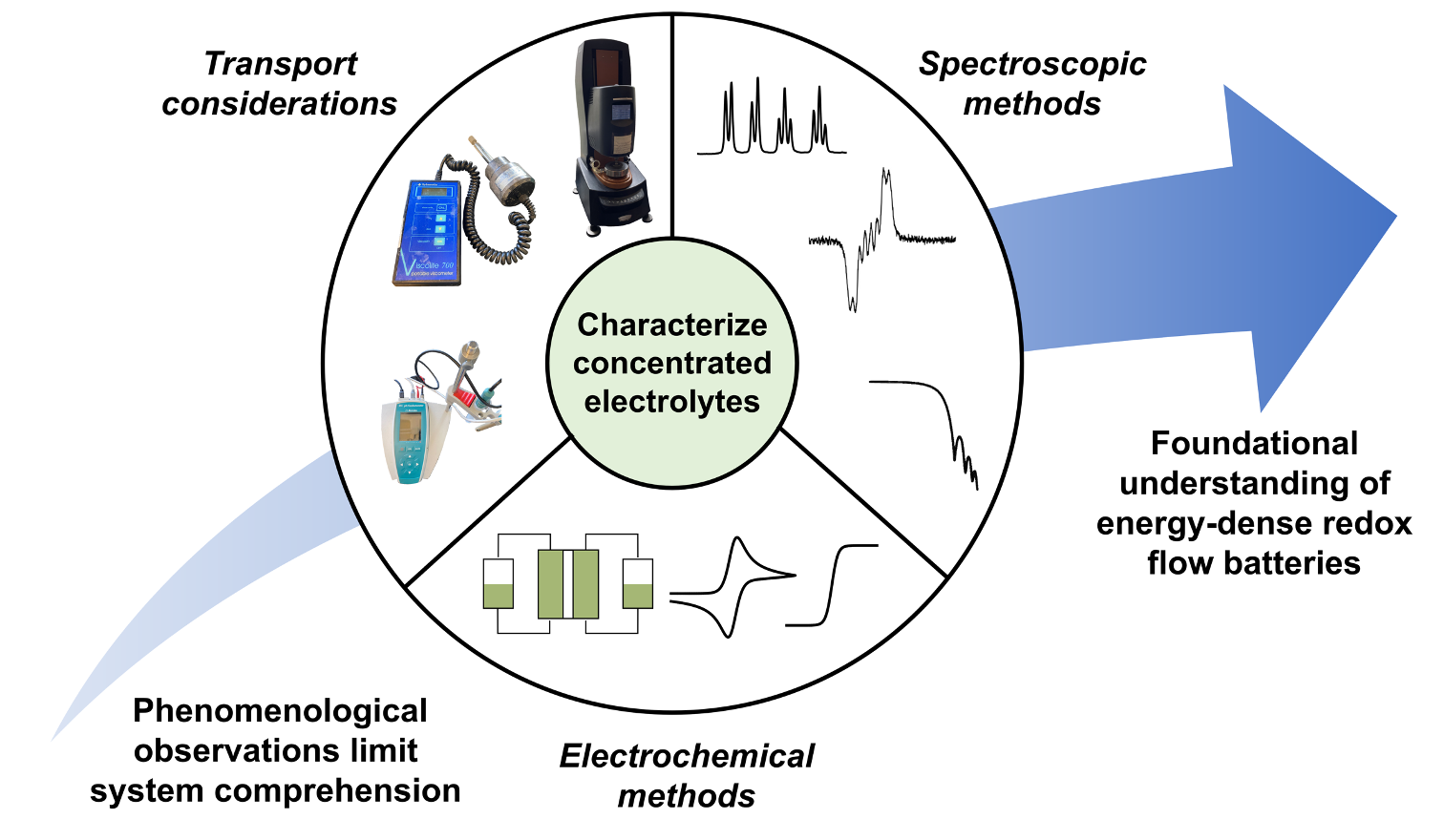
On the challenges of materials and electrochemical characterization of concentrated electrolytes for redox flow batteries
This perspective highlights the status of, and propose future approaches for, rheological, electrochemical, and spectroscopic characterization of electrolytes with high concentrations of redox-active analytes for energy storage, with an emphasis on nonaqueous redox flow batteries (RFBs). Read More
-
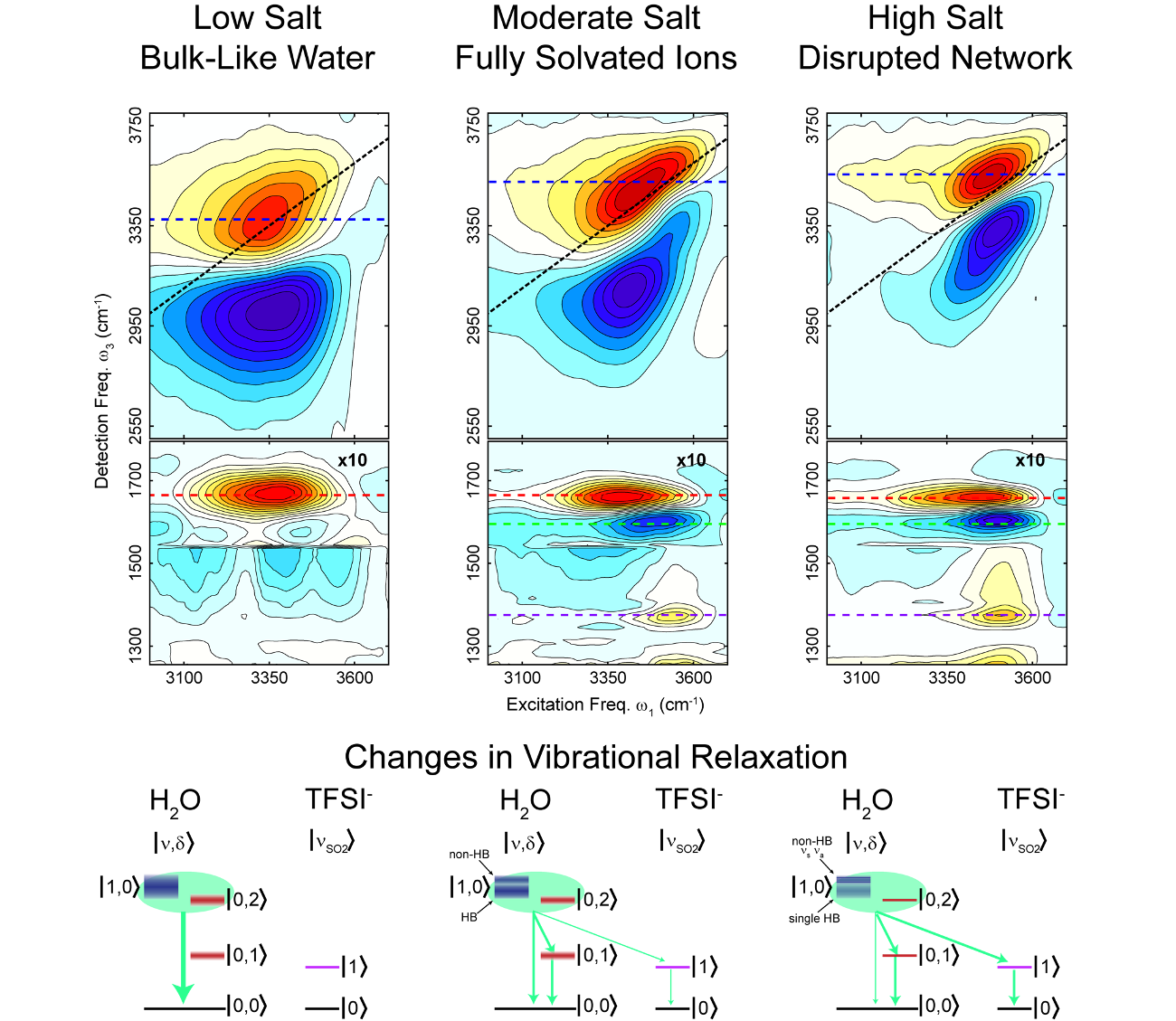
From Networked to Isolated: Disrupting Water Hydrogen Bonds in Superconcentrated Electrolytes
Using ultrafast infrared spectroscopy and molecular dynamics simulations we uncover details of the molecular-scale structure of super-concentrated aqueous electrolytes. Read More
-
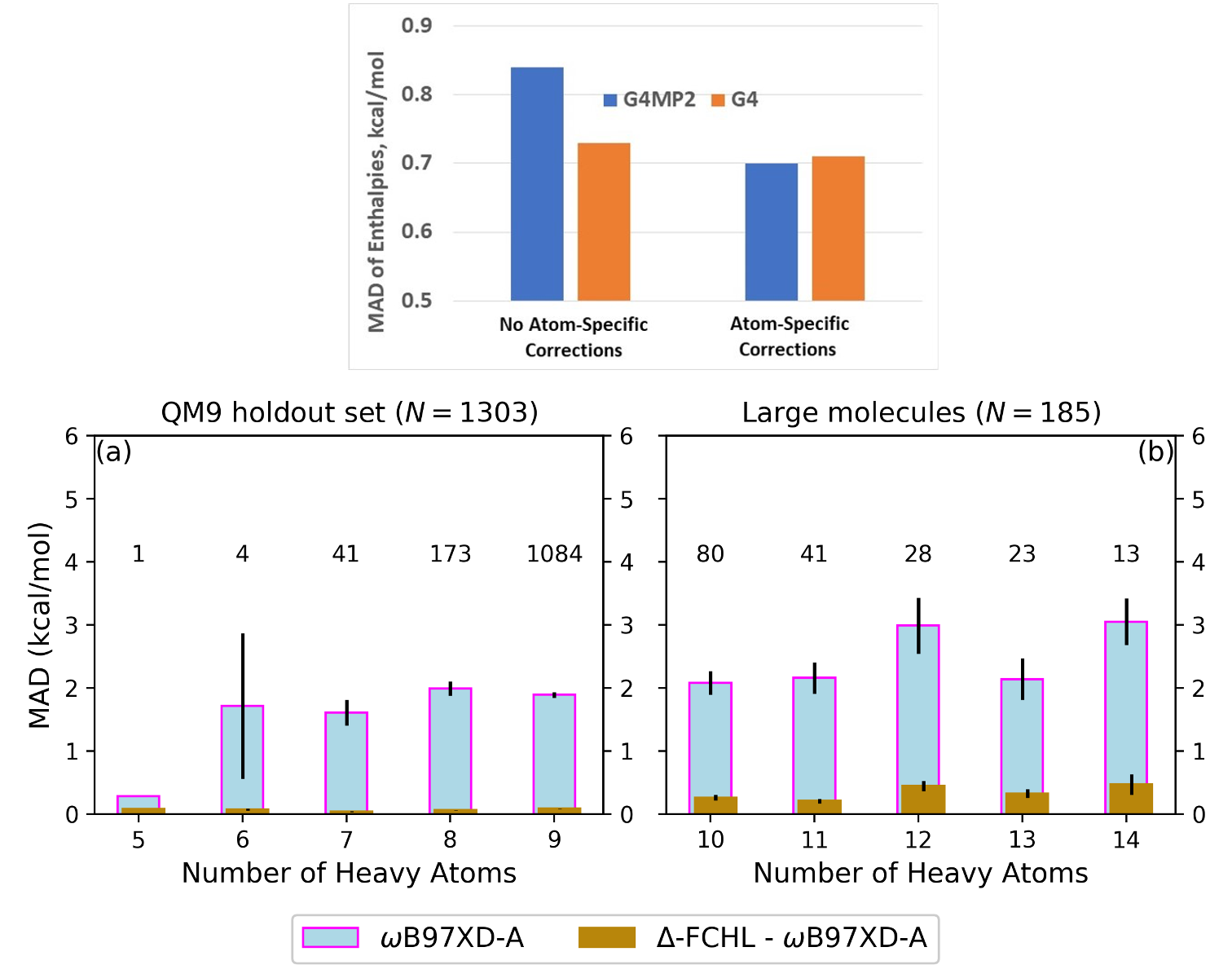
IMPROVING ACCURACY OF COMPOSITE METHODS: A G4MP2 METHOD WITH G4-LIKE ACCURACY AND IMPLICATIONS FOR MACHINE LEARNING
This work introduces a new method to improve quantum chemical predictions of energies of large organic molecules that can also be used in combination with machine learning to predict molecular energies at a much lower cost of computer time. Read More
-
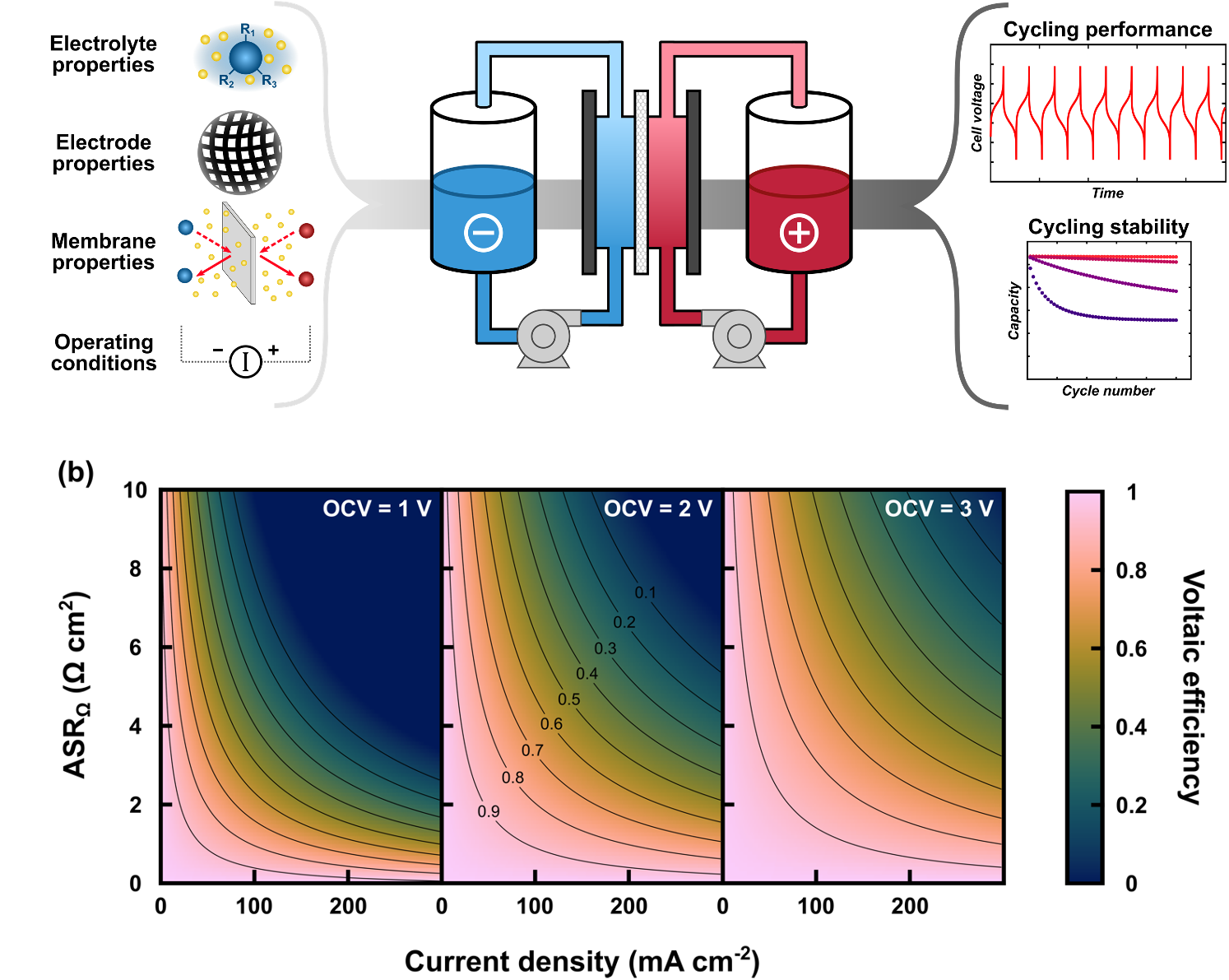
Connecting material properties and redox flow cell cycling performance through zero-dimensional models
We derived a zero-dimensional, analytical model for describing mass balances and cell voltages in redox flow batteries (RFBs), enabling direct connections between material / electrolyte properties, cell operating conditions, and resulting performance metrics (e.g., energy efficiency, capacity fade). Read More
-
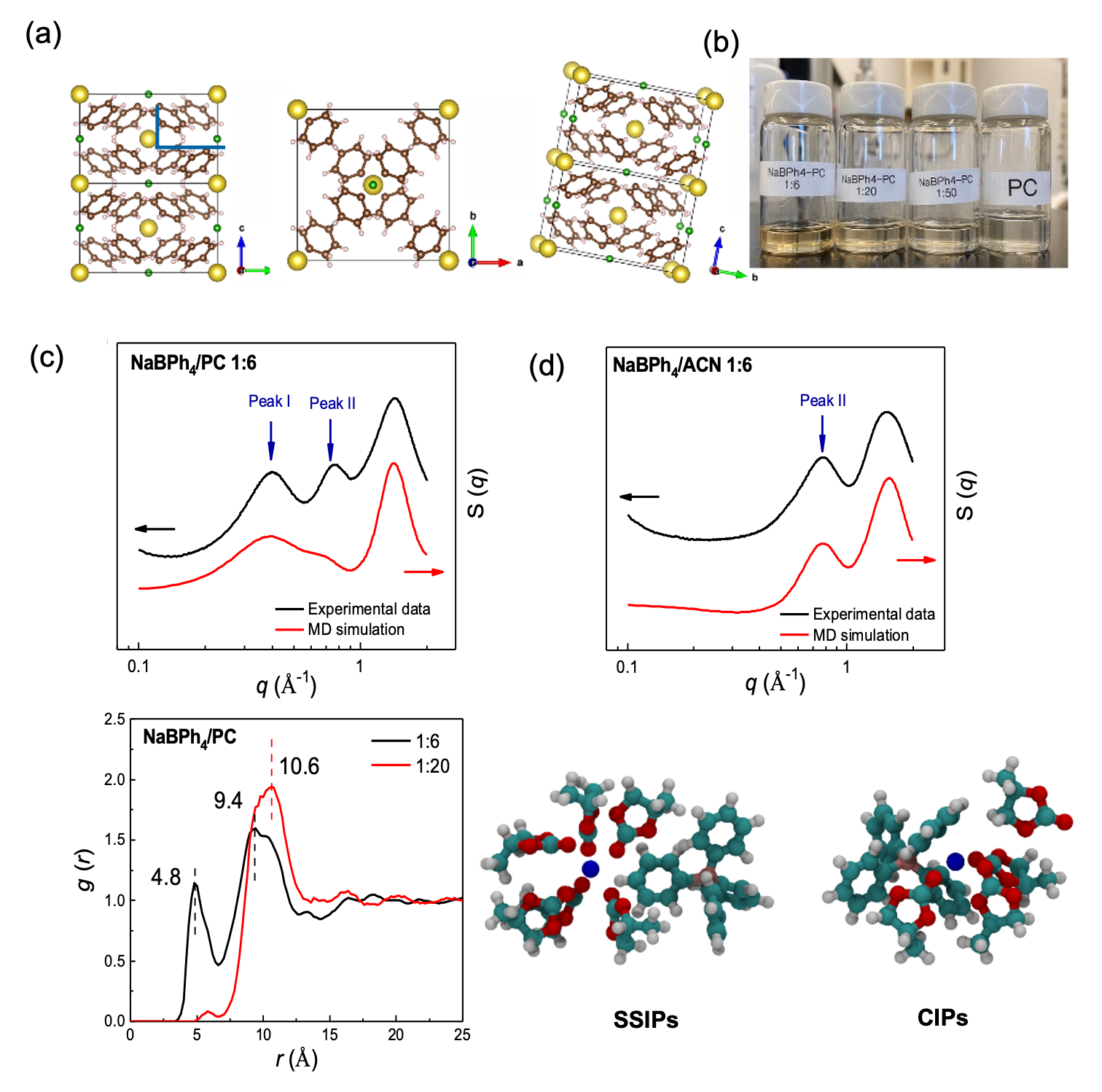
Understanding fluorine-free electrolytes via small-angle X-ray scattering
We compare the solvation phenomenon of sodium tetraphenylborate (NaBPh4) salt dissolved in organic solvents of propylene carbonate (PC), 1,2-dimethoxyethane (DME), acetonitrile (ACN) and tetrahydrofuran (THF) by SAXS/WAXS measurement and MD simulation. Read More
-
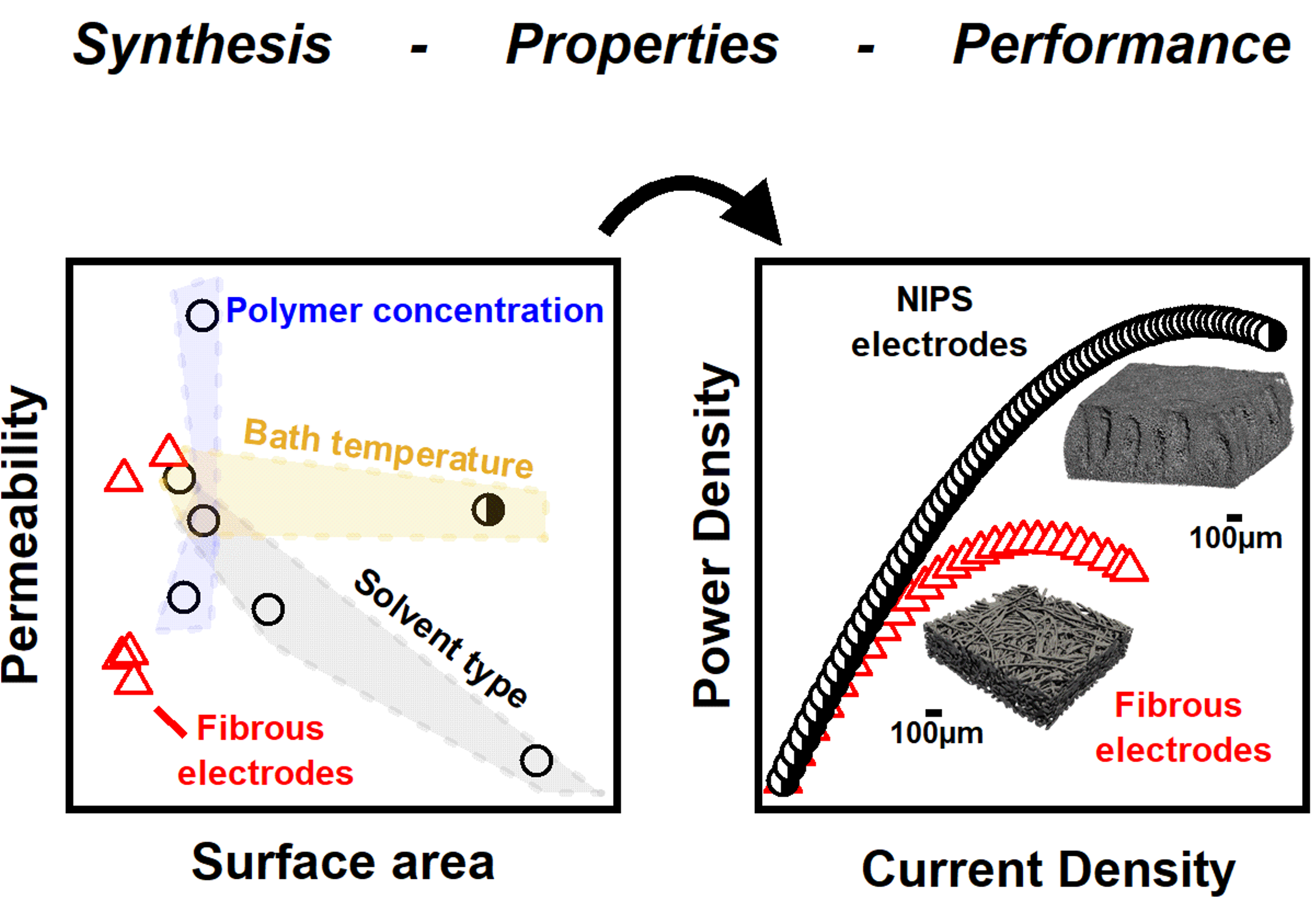
Microstructural engineering of high-power redox flow batteries via non-solvent induced phase separation
Non-solvent induced phase separation (NIPS) is used to develop electrode synthesis-structure-performance relationships, and select samples are incorporated in redox flow batteries (RFBs) which exhibit high power density. Read More
-
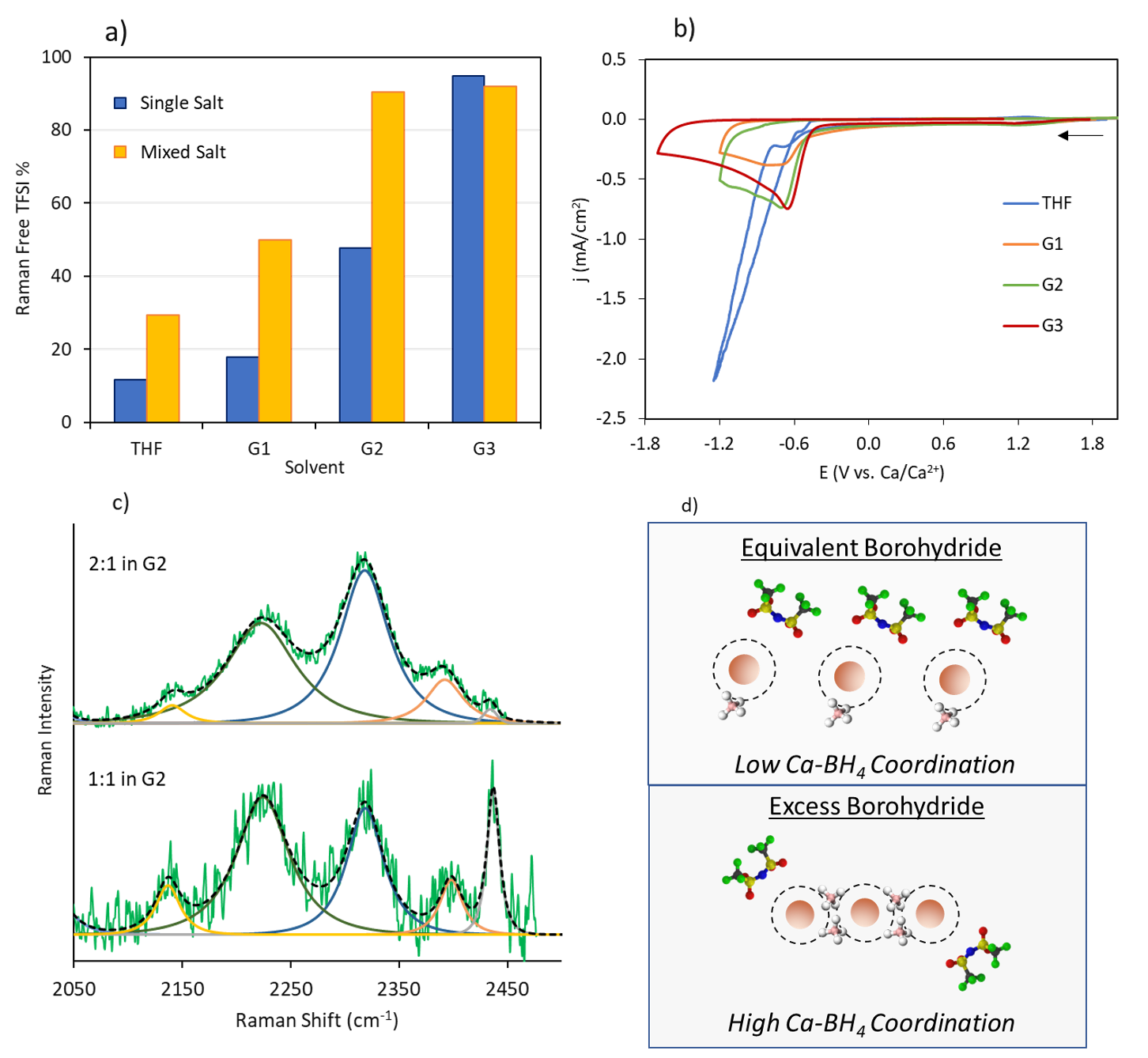
Efficacy of Stabilizing Calcium Battery Electrolytes through Salt-Directed Coordination Change
The factors determining the extent to which salt anions can be stabilized during Ca plating by eliminating their coordination with Ca2+ through co-salt addition were elucidated. Contrary to expectation, the exemplar bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide (TFSI-) anion is unstable whether in the coordinated or free state. Instead, the type of Ca2+ coordination structure formed with the co-salt anion determines whether Ca deposition can be achieved. Read More
Latest Updates
-
You’re Invited - JCESR and Beyond: Translating the Basic Science of Batteries
Please join us at Argonne National Laboratory on Tuesday, April 4, 2023 for JCESR and Beyond: Translating the Basic Science of Batteries. Registration is now open. This in-person event will celebrate 10 years of research from the Joint Center… Read More
-
A Message from JCESR: In Memory of George Crabtree
It is with heavy hearts that we say goodbye to George Crabtree, a Senior Scientist and Distinguished Fellow at Argonne National Laboratory, and Director of the Joint Center for Energy Storage Research (JCESR), who passed away unexpectedly on January 23. Dr. Read More
-
Cyanopyridines As Extremely Low-Reduction-Potential Anolytes for Nonaqueous Redox Flow Batteries
Discovery of a cyanophenylpyridine derivative with a very low reduction potential and good stability during cycling. Read More
-
Characterizing Redoxmer – Electrode Kinetics Using a SECM-Based Spot Analysis Method
Identified asymmetries in electron transfer (ET) kinetics between the reduction and oxidation of ferrocene-based redoxmers by measuring the ET rate constants (kf/kb) as a function of electrode potential. Read More
-
Benzotriazoles as Low Potential Anolytes for Non-Aqueous Redox Flow Batteries
We developed an easy-to-synthesize benzotriazole-based anolyte with a high energy redox potential (-2.3 V vs Fc/Fc+) and high solubility that demonstrates stable electrochemical cycling performance. Read More

