Scientific Achievement
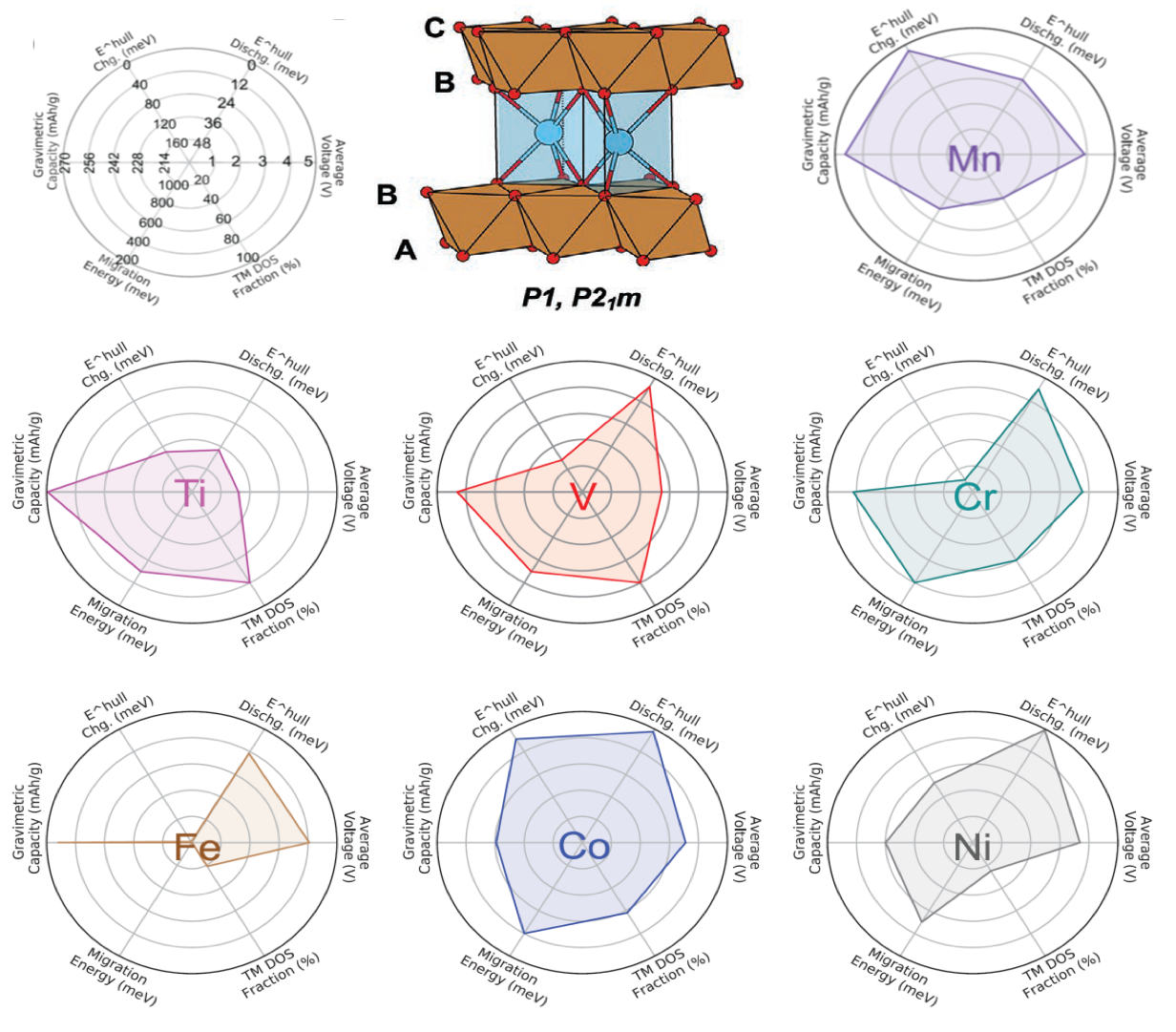
First-principles calculations are used to demonstrate that P-type layered CaTM2O4 materials with a range of TM substitutions (TM = Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, and Ni) have excellent battery-related properties including thermodynamic stability, average voltage, energy density, synthesizability, ionic
mobility, and electronic structure.
Significance and Impact
- This class of layered CaTM2O4 materials may open up a tremendous design space for the future of cathode materials for Ca batteries.
Research Details
- We assessed their thermodynamic stability, average intercalation voltage, energy density, preference for intercalation versus conversion, synthesizability, cation mobility, and electronic structure.
- Substituting TM was shown as an effective strategy to reduce Co content. Mixing some Co with Ni can compensate the drawbacks of CaNi2O4 by increasing the thermodynamic stability of the charged phase and the redox activity of TM ion.

