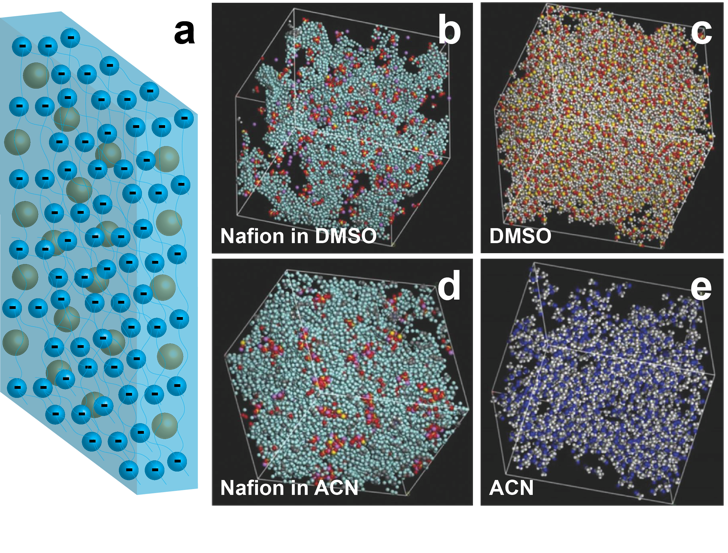
Scientific Achievement
Successfully predicted the ionic conductivities of lithiated Nafion membranes swollen in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and acetonitrile (ACN) using molecular dynamics and experimentally validated the results.
Significance and Impact
This work demonstrated that the ionic conductivity of Nafion is substantially governed by the concentration of free Li+, i.e. by the degree of dissociation of the Li+ and RSO3- pairs, and that the inherent mobility of Li+ in different solvents is of secondary importance.
Research Details
- A molecular dynamic model of lithiated Nafion swollen in the nonaqueous solvents DMSO and ACN was developed.
- The model predicts that the degree of dissociation of Li+ and RSO3- in Nafion + DMSO is about 64%, while the degree of dissociation in Nafion + ACN is close to 0.
- The calculated Li-N117 conductivities in DMSO and ACN are in good agreement with the experimental values.

