Scientific Achievement
Obtained a deeper understanding of the chemical and electrochemical stability governing the suitability of several organic solvents commonly considered for Mg battery electrolytes.
Significance and Impact
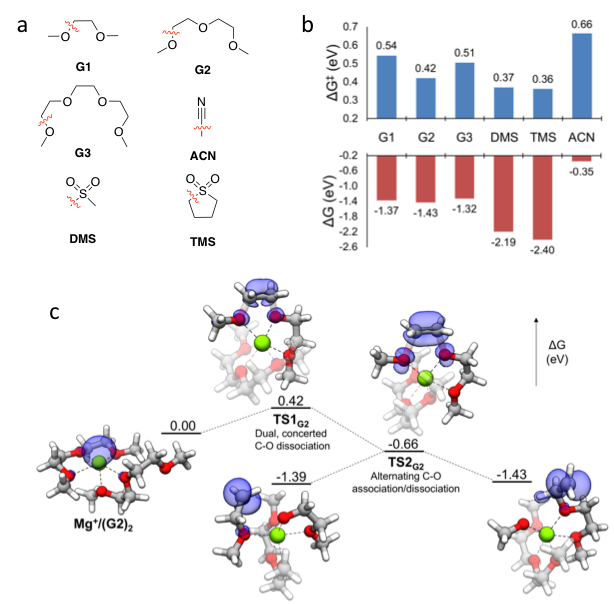
First principles calculations were used to determine the stability of organic solvents in Mg battery electrolytes during plating conditions. We accomplish this by finding decomposition reaction pathways for solvents while coordinated to the transient Mg+ ion formed during plating. We find that all solvents considered exhibit exergonic decomposition pathways; consequently, their stability depends on the kinetic barrier to decomposition and/or reduction of solvent by Mg+. The order of stability follows glymes > sulfones > acetonitrile, in accordance with general experimental observations.
Research Details
First-principles evaluation of chemical and electrochemical stability of organic solvents during Mg plating
Determination of intrinsic stability against direct reduction by Mg metal for all solvents considered
Location of decomposition reaction profiles of solvent molecules in a first solvation shell coordinated to Mg+

