Scientific Achievement
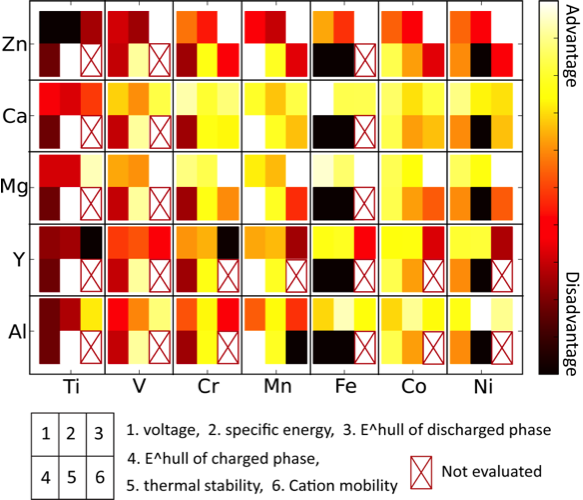
A high-throughput strategy to systematically screen multivalent cathode materials based on comprehensive computational first-principles property evaluations has been developed and has been used to identify Mn2O4 as a feasible host candidate, with Ca2+ and possibly Mg2+ as mobile cations
Significance and Impact
The study provided an important down-select from 35 possible materials to two, focusing the experimental teams on the most promising candidates. In addition, important design metrics involving the size of the mobile cation and available site coordination in the host structure were obtained to guide future screening
Research Details
- Our evaluation provided the largest-to-date systematic computational screening of multivalent intercalation compounds and has given valuable insights to the limiting factors guiding future efforts
- Screening criteria included insertion voltage, capacity, thermodynamic and thermal stability, volume expansion and the intercalating ion mobility using first-principles calculations
Work performed at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (JCESR partner) and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (JCESR Collaborator) Miao Liu, Ziqin Rong, Rahul Malik, Piero Canepa, Anubhav Jain, Gerbrand Cederb and Kristin Persson, Energy & Environmental Science, 2015.
DOI: 10.1039/c4ee03389b

