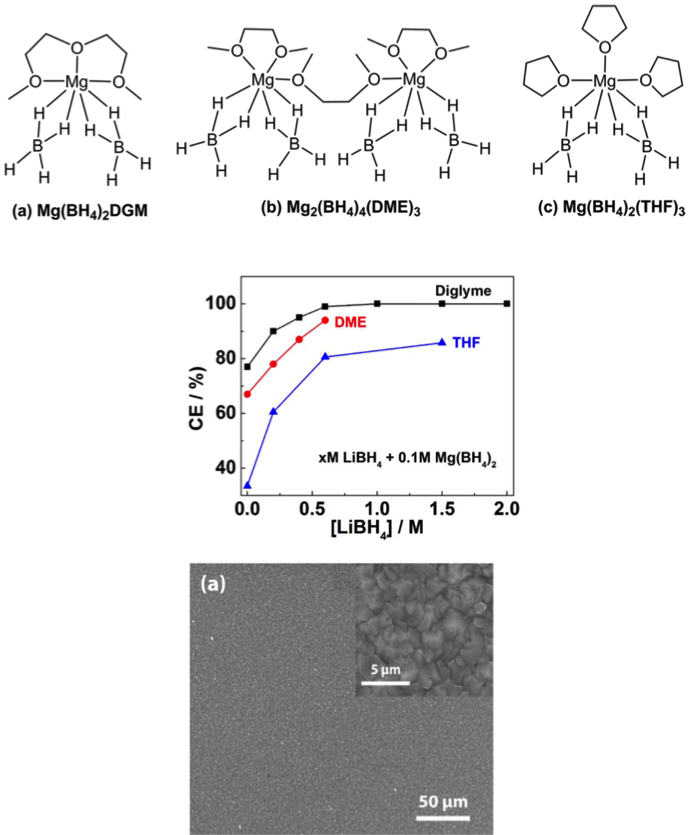
(Middle) Electrochemical performance of electrolytes (CE=coulombic efficiency); CE correlated closely with the solvents and additive (LiBH4) which is translated into the solution coordination structures. The highest CE could reach 100%.
(Bottom)SEM images of Mg deposition from the Mg electrolyte: smooth and dendrite-free morphology.
Scientific Achievement
- Identification of the solution coordination structures of Mg(BH4)2 through a simple NMR method.
- Direct correlation of the solution coordination structures with electrochemical characteristics.
Significance and Impact
- This work provides a simple method to identify the solution complex structures of Mg electrolytes.
- The identification of the structure-property relationship could provide guidance for the design of new Mg electrolytes and tuning properties of existing electrolytes.
Research Details
- The solution coordination structures of Mg(BH4)2 in different ethers solvents have been identified.
- The ligand effects on Mg electrolyte properties have been investigated and understood.
- A new electrolyte with near 100% Coulombic efficiency and smooth, dendrite-free Mg deposition is developed.
- A rechargeable Mg cell based on the new electrolyte has been demonstrated.
Y. Shao, T. Liu, G. Li, M. Gu, Z. Nie, M. Engelhard, J. Xiao, D. Lv, C. Wang, J. Zhang, and J. Liu. Yuyan Shao, Tianbiao Liu, Guosheng Li, Meng Gu, Zimin Nie, Mark Engelhard, Jie Xiao, Dongping Lv, Chongmin Wang, Ji-guang Zhang, and Jun Liu. PNNL. Scientific Reports, 2013.

