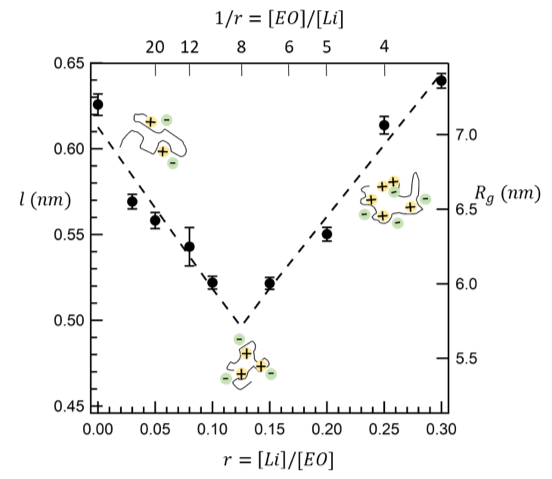
Scientific Achievement
The effect of salt concentration on the molecular conformation of a polymer was determined by small angle neutron scattering.
Significance and Impact
Polymer electrolytes are important as they provide platform for the development of intrinsically safe rechargeable lithium batteries. It is well-known that the oxygen atoms on the polymer backbone can solvate and coordinate with Li+ ions. We show that the polymer conformation is highly dependent on salt concentration, which affects ion transport.
Research Details
- Quantified the effect of salt concentration on the radius of gyration of polymer chains, poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO), with a dissolved lithium salt. Since the polymer chains size is proportional to the square root of the number of monomers, our results can be used to predict the effect of salt on a statistical segment length, l, which is in effect the proportionality constant.
- Our analysis is the first study in the field of neutron scattering from polymers to account for volume changes of mixing, a parameter that is non-negligible in all electrolytes.

