Scientific Achievement
This study underscores the need to match the stability testing conditions for a phenothiazine electroactive derivative for RFB application. For analysis of stability, RRDE voltammetry can be used to rapidly screen molecules over seconds or minutes, providing stability trends that are similar to results that require several weeks to obtain using UV−vis spectroscopy.
Significance and Impact
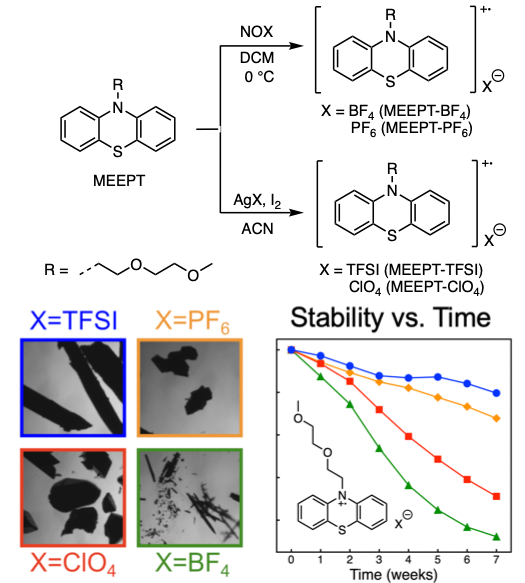
Chemical environment plays an important role in determining the overall stability of a glycolated phenothiazine (MEEPT) in its charged form. Counter-ion identity/electrolyte composition dictate the stability of these in solution and solid state.
Research Details
- MEEPT-X radical cation salts can be isolated as crystalline solids.
- For four different salts, with counterions BF4−, PF6−, ClO4−, and TFSI−, we determined the effect of counterion identity on the stability of the MEEPT-X in solution and in the solid state.
- Long-term solution-based stability results from UV−vis measurements showed similar trends to solution-based stability results from RRDE voltammetry.
- In the solid-state, these salts are shelf stable and exhibit high thermal stability.

