Scientific Achievement
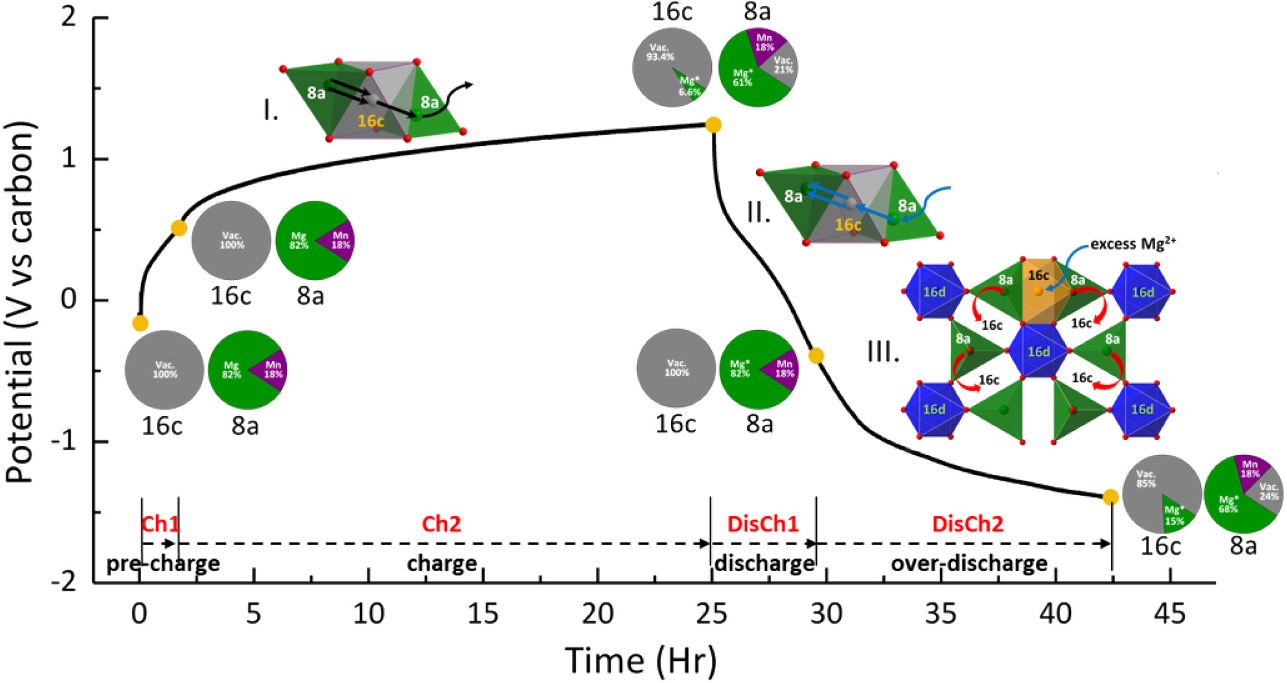
The Mg-ion migration mechanisms in MgMnCrO4 spinel cathode was investigated experimentally through operando x-ray diffraction revealing a complex mechanism during Mg insertion/extraction.
Significance and Impact
Previous research showed the spinel cathode, MgMnCrO4, as a promising high-voltage cathode material with reversible insertion of Mg ions. However, the relationship between inversion defects and the migration mechanisms of cations during cycle was not understood.
Research Details
- MgMnCrO4 was measured and studied structurally through synchrotron diffraction, utilizing a custom operando x-ray diffraction cell.
- Operando diffraction revealed a complex reorganization of cations during charging and discharging. This cation migration couples with inversion defects and structure of the lattice.
- Combining the operando diffraction with DFT computations revealed how the details of cation migration and lattice defects elucidate the nature of reversibility, voltage hysteresis and capacity loss

