Scientific Achievement
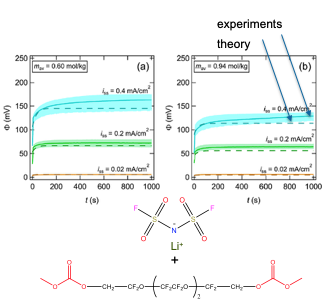
Experimentally measured ion transport rate in a fluorinated electrolyte is in quantitative agreement with theory from the dilute limit up to the salt solubility limit.
Significance and Impact
Fluorinated electrolytes have the potential to serves as electrolytes in future lithium batteries due to their low flammability. Ion transport in dilute solutions occurs due to transport of individual ions. In concentrated solutions, ion transport is dominated by clusters in close contact with each other. A single set of parameters enables prediction of the voltage-current characteristics of the electrolyte in symmetric cells.
Research Details
- Independently determined conductivity, salt diffusion coefficient, Li+ transference number, and the thermodynamic factor were used to predict ion transport.
- The limiting current is a non-monotonic function of salt concentration. It decreases with increasing concentration near the solubility limit.

