Scientific Achievement
In situ and ex situ characterization is combined with electrochemical analysis to elucidate mass transport and fluid dynamic relationships in carbon cloth electrodes with different weave patterns (plain, 8-satin harness, and 2×2 basket).
Significance and Impact
1071 HCB plain weave cloth electrode exhibits a favorable balance of hydrodynamic and polarization performance in non-aqueous flow battery with a kinetically-facile redox couple.
Research Details
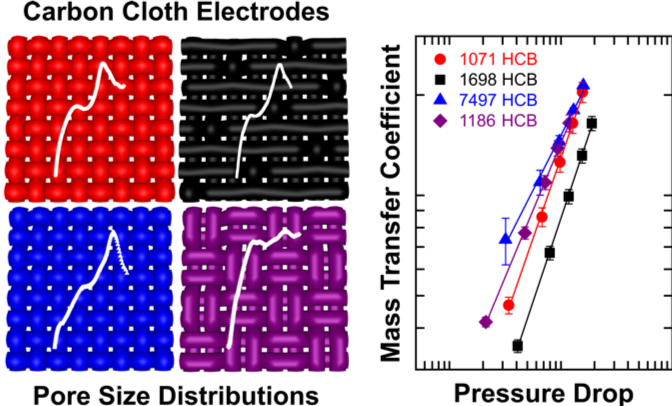
- Mercury intrusion porosity pore size distribution plots depict the unique microstructures for four woven materials. All cloth electrodes were fabricated from the same 7.5 µm diameter carbon fiber.
- The electrochemical and fluid dynamic experiments were conducted in a single electrolyte flow cell architecture.
- The hydrodynamics and the mass transfer comparison show that the plain weave pattern possesses a favorable structure for both phenomena.

