Scientific Achievement
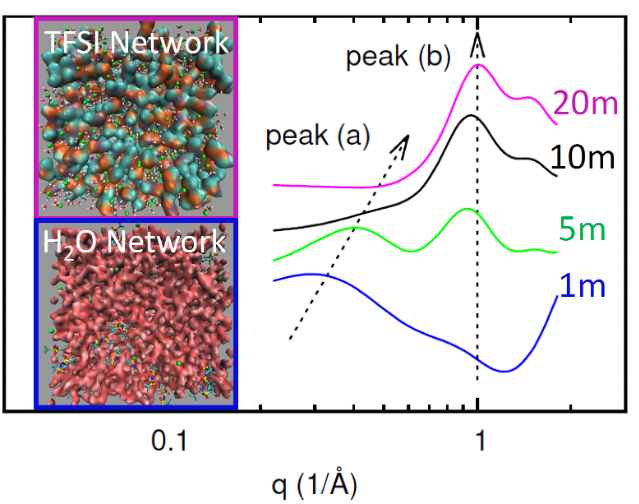
In the highly concentrated 20 m LiTFSI solution, the water network existing in low concentration aqueous electrolytes is completely broken and is replaced by a TFSI- network; in spite of local heterogeneity, the liquid structure is homogeneous in general instead of forming TFSI- rich or water rich domains.
Significance and Impact
The proposed liquid structure is fundamentally different from those suggested previously and indicates that the observed high apparent transference number of Li+ is due to mechanisms that needs further study.
Research Details (18pt Arial, Bold)
- X-ray total scattering and FTIR experiments were perfomed for LiTFSI aqueous electrolyte as a function of LiTFSI concentration.
- Classical molecular dynamics (CMD) simulation was also carried out for the same electrolytes and the calculated results agree with experiments quantitatively, therefore validated the accuracy of the simulations.
- Detailed liquid structure was analyzed based on the validated CMD simulations.

