Chemical Transformation
-
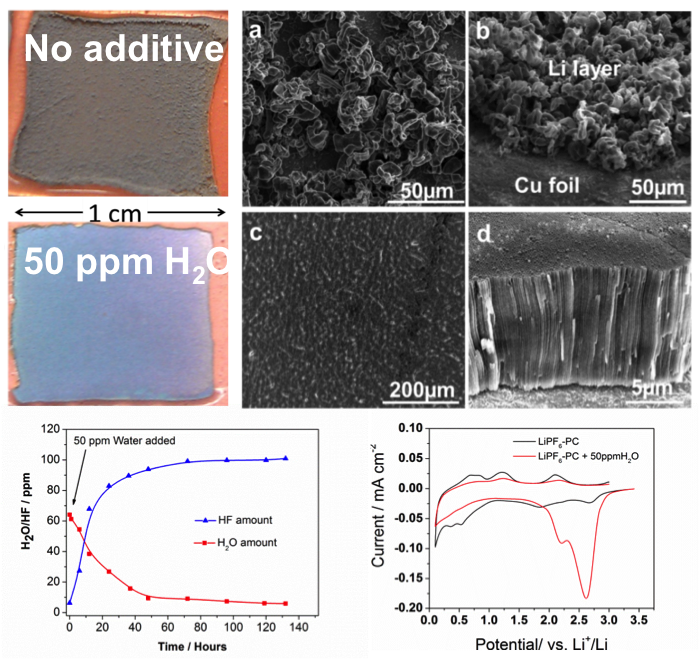
Dendrite-Free Li Deposition Using Trace-Amounts of Water as an Electrolyte Additive
Residual water (H2O) present in nonaqueous electrolytes has been widely regarded as a detrimental factor for lithium (Li) batteries. However, dendrite-free Li film can be obtained with trace H2O as an electrolyte additive. Read More
-
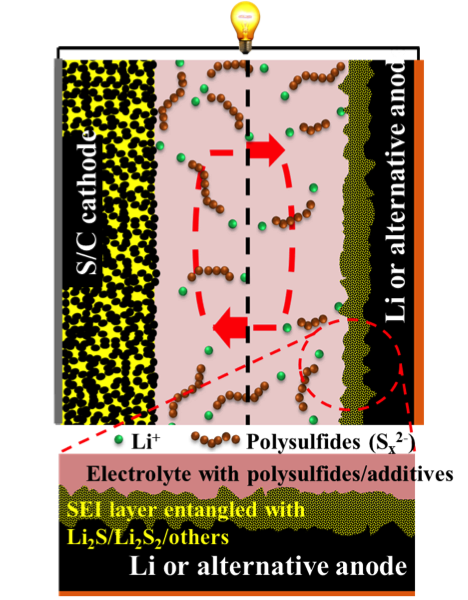
Anodes for Rechargeable Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
Recent developments on the protection of the Li metal anode in Li-S batteries are reviewed Read More
-
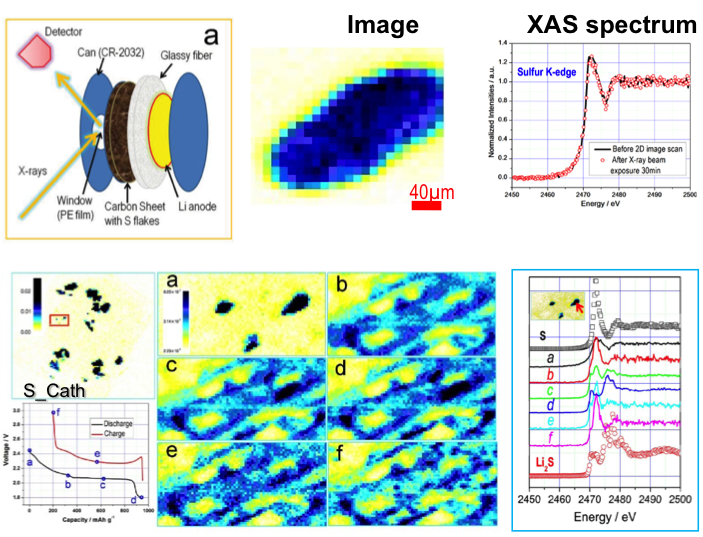
Direct Observation of the Redistribution of Sulfur and Polysufides in Li-S Batteries by In Situ X-Ray Fluorescence Microscopy
The dissolution and redistribution of sulfur and polysulfides were directly observed by XRF imaging. The long-chain polysulfides were generated as soon as discharge was initiated. The dissolved polysulfide diffused to the anode side and deposited onto (and reacted with) lithium metal. Read More
-
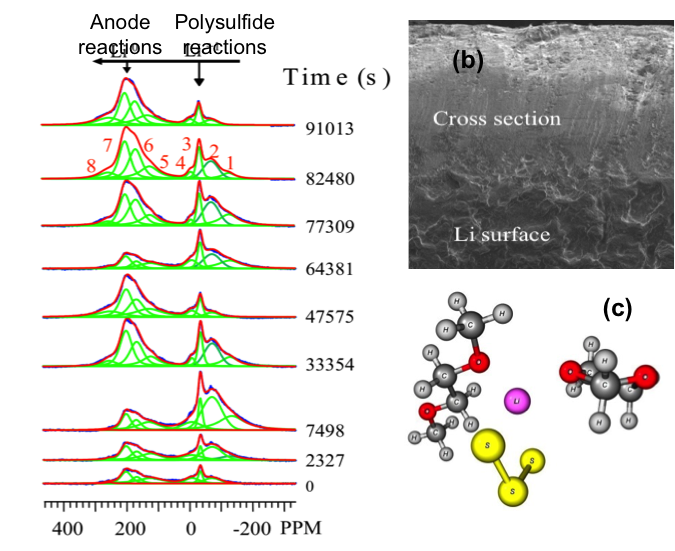
Following the Transient Reactions in Lithium-Sulfur Batteries Using an In Situ Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Technique
First in situ NMR characterization of the full cell electrochemical reactions in Li-S batteries using a microbattery design Read More
-
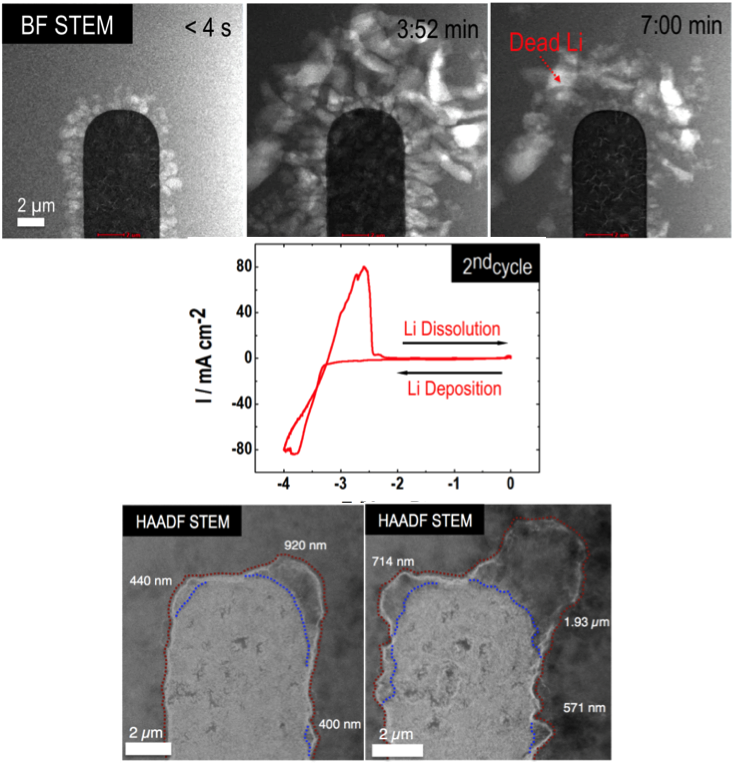
Direct Observation of SEI and Dendrite Dynamics by Operando Electrochemical Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy
Implemented “battery in a STEM” - an operando electrochemical stage inside an Cs-corrected scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM) Read More
-
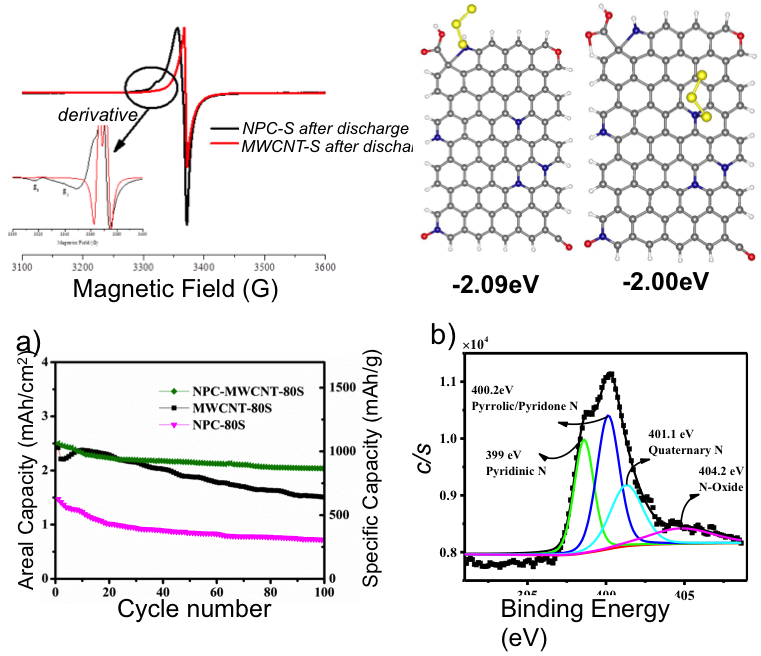
Molecular‐Confinement of Polysulfide within HybridElectrodes for High Mass Loading in Lithium Sulfur Batteries
N-doped carbon stabilizes the S3 radicals, which are rarely detected in ether-based electrolyte due to their high reactivity; this also restrains the polysulfide loss during battery cycling. Read More
-
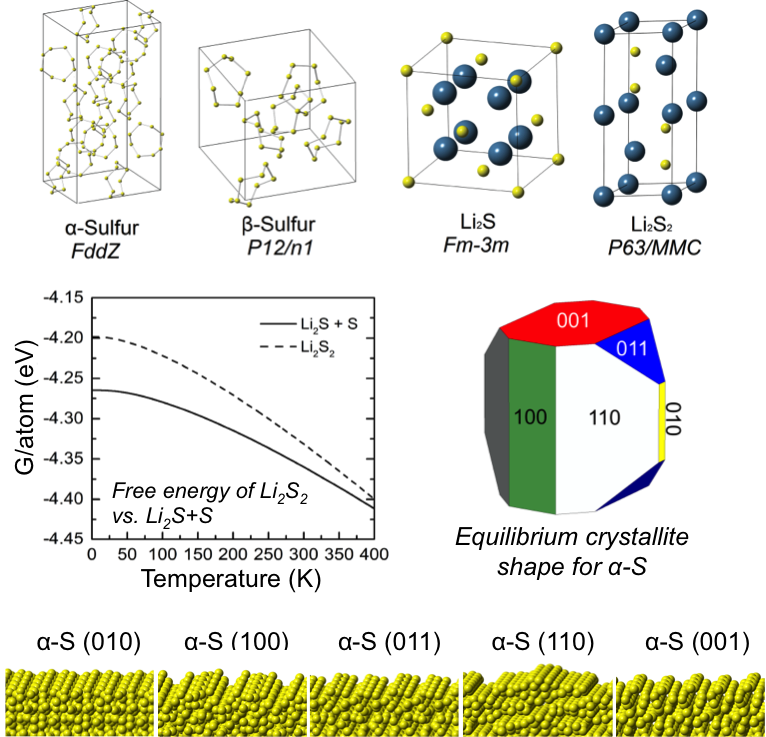
First-Principles Study of Redox End-Members in Li-Sulfur Batteries
Van der Waals-augmented density functional theory (vdW-DF), quasi-particle methods (G0W0), and continuum solvation techniques were used to predict several structural, thermodynamic, spectroscopic, electronic, and surface characteristics of solid-phase redox end-members in Li-S batteries. Read More
-
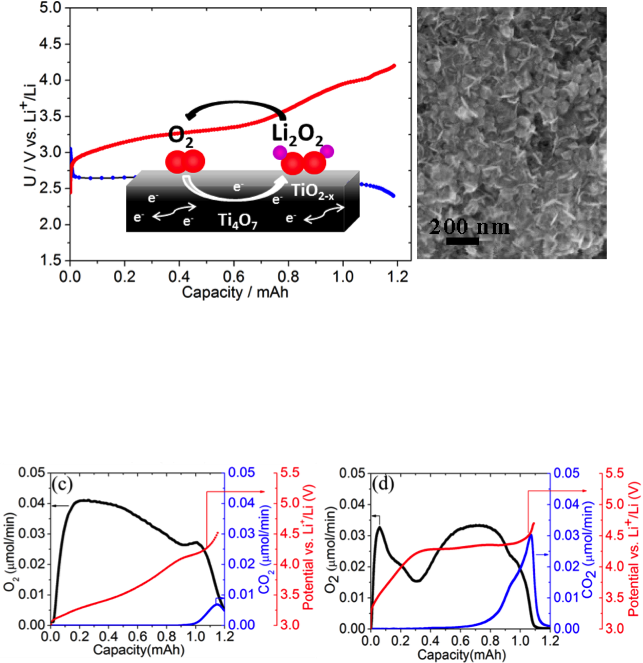
A Highly Active Nanostructured Metallic Oxide Cathode for Li-O2 Batteries
Synthesis of a low-cost nanocrystalline metallic metal oxide that shows very good ORR/OER properties in a Li-O2 cell, highlighting the importance of controlling the cathode interface to achieve better round-trip efficiency Read More
-
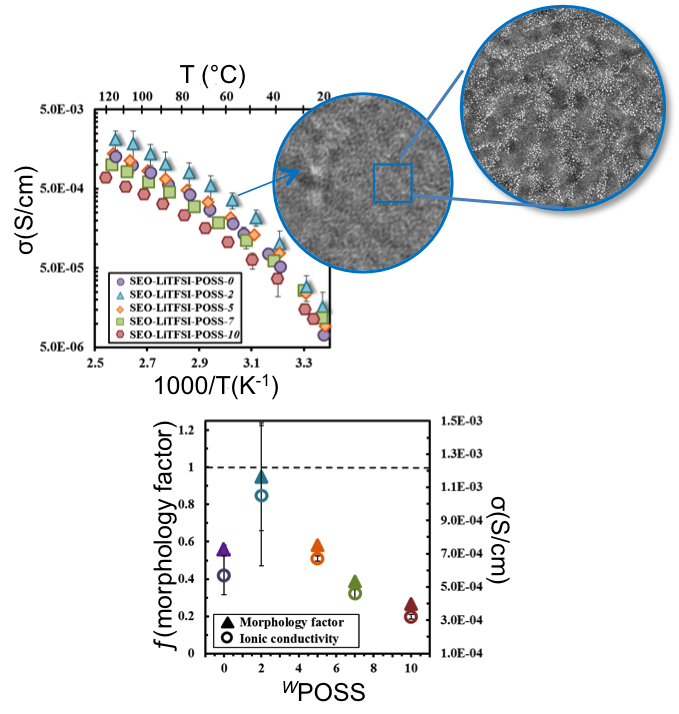
Nanoparticle-Driven Assembly of Highly Conducting Hybrid Block Copolymer Electrolytes
The ionic conductivity of nanostructured SEO block copolymer electrolytes is closely related to the morphology Read More
-
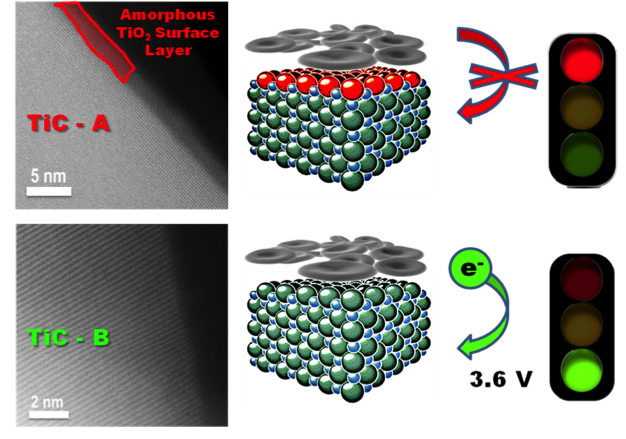
Electrode Interface Dictates Oxygen Evolution from Lithium Peroxide in Li-O2 Batteries
Identification of the critical role the surface properties of metallic TiC & TiN supports play in Li-O2 electrochemistry. Oxygen evolution from bulk Li2O2 is enabled by "clean" surfaces but completely inhibited by 2-3 nm thick TiO2 films. Read More
Latest Updates
-
You’re Invited - JCESR and Beyond: Translating the Basic Science of Batteries
Please join us at Argonne National Laboratory on Tuesday, April 4, 2023 for JCESR and Beyond: Translating the Basic Science of Batteries. Registration is now open. This in-person event will celebrate 10 years of research from the Joint Center… Read More
-
A Message from JCESR: In Memory of George Crabtree
It is with heavy hearts that we say goodbye to George Crabtree, a Senior Scientist and Distinguished Fellow at Argonne National Laboratory, and Director of the Joint Center for Energy Storage Research (JCESR), who passed away unexpectedly on January 23. Dr. Read More
-
Cyanopyridines As Extremely Low-Reduction-Potential Anolytes for Nonaqueous Redox Flow Batteries
Discovery of a cyanophenylpyridine derivative with a very low reduction potential and good stability during cycling. Read More
-
Characterizing Redoxmer – Electrode Kinetics Using a SECM-Based Spot Analysis Method
Identified asymmetries in electron transfer (ET) kinetics between the reduction and oxidation of ferrocene-based redoxmers by measuring the ET rate constants (kf/kb) as a function of electrode potential. Read More
-
Benzotriazoles as Low Potential Anolytes for Non-Aqueous Redox Flow Batteries
We developed an easy-to-synthesize benzotriazole-based anolyte with a high energy redox potential (-2.3 V vs Fc/Fc+) and high solubility that demonstrates stable electrochemical cycling performance. Read More

