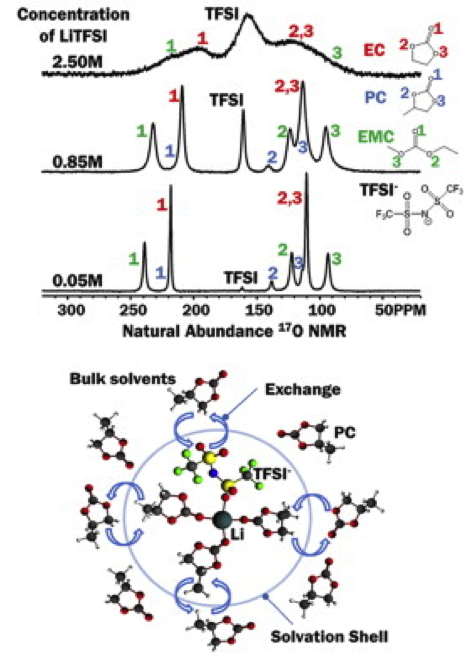
(Bottom) The solvation structure of LiTFSI derived from the results obtained by both NMR and quantum chemistry calculations
Scientific Achievement
- A high sensitivity NMR probe was developed at ultra-high field, allowing 17O NMR spectra on electrolytes acquired at concentration as low as about 20 mM.
- The solvation structures of LiTFSI in solvents of EC, PC, and EMC, including mixtures of these solvents were separately investigated.
Significance and Impact
- A Li+ ion is coordinated with four double bond oxygen atoms.
- In the case of excessive amount of solvents of EC, PC and EMC, the Li+ coordinated solvent molecules are undergoing quick exchange with bulk solvent molecules.
- For LiTFSI concentration between low and saturation, (LiTFSI)(PC)3 for LiTFSI in PC, and (LiTFSI)(EMC)3 for LiTFSI in EMC are the preferred structures.
- At high LiTFSI concentrations, in particular at saturated concentrations, (LiTFSI)2(PC)4 for LiTFSI in PC, and (LiTFSI)2(EMC)3 for LiTFSI in EMC are the preferred structures.
Research Details
- A high sensitivity natural abundance 17O NMR probe was developed.
- 17O NMR spectra on pure solvents of EC, PC and EMC, LITFSI dissolved in PC, in EMC, and in a mixture of PC+EMC, EC+PC+EMC were acquired.
- Quantum chemistry calculations of the 17O chemical shifts on various solvation structures were carried out and compared with experimental values.
Worked performed at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (JCESR partner) by Deng X, MY Hu, X Wei, W Wang, Z Chen, J Liu, and JZ Hu, Journal of Power Sources, 2015.

