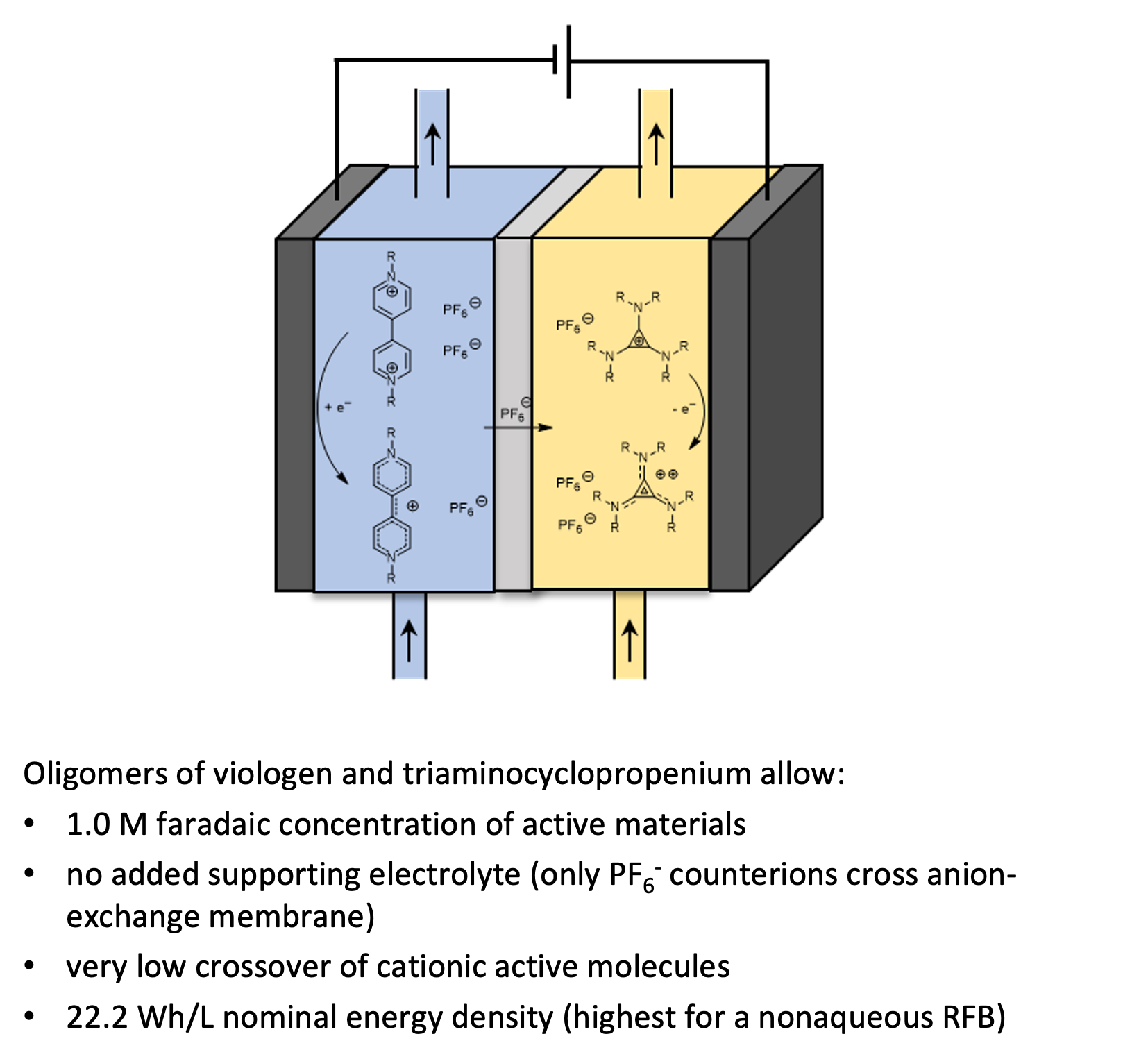
Scientific Achievement
Oligomers of permanently cationic anolyte and catholyte molecules allow the assembly of high energy density nonaqueous redox flow batteries with little crossover of active materials.
Significance and Impact
High energy density is desirable in nonaqueous RFBs, and they still fall short of aqueous vanadium RFBs. With oligomers of permanently cationic active molecules, nonaqueous RFBs with a nominal energy density of 22.2 Wh/L were constructed.
Research Details
- Trimeric viologen and triamino-cyclopropenium were used to make a RFB in CH3CN with 1.0 M faradaic concentration and 22.2 Wh/L nominal energy density.
- The cationic oligomers led to very little crossover across the anion-exchange membrane in the asymmetric battery. There was no supporting electrolyte, and only PF6- counterions cross membrane during cycling.

