Scientific Achievement
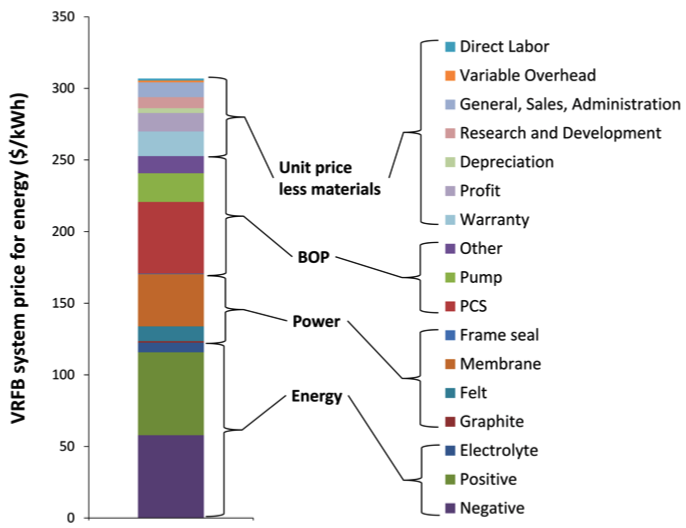
This work conducted a techno-economic analysis of a prospective production process for an aqueous all vanadium flow battery and a nonaqueous lithium polysulfide flow battery.
Significance and Impact
Redox flow batteries have potential advantages to meet the stringent cost target for grid applications. However, the manufacturing process and therefore potential high-volume production price of redox flow batteries is largely unquantified.
Research Details
- The estimated investment and variable costs are translated to fixed expenses, profit, and warrant as a function of production volume.
- When compared to lithium-ion batteries, redox flow batteries are estimated to exhibit lower costs of manufacture owing to their simpler reactor (cell) design, lower required area, and thus simpler manufacturing process.
- Redox flow batteries are also projected to achieve the majority of manufacturing scale benefits at lower production volumes as compared to lithium-ion.
Work performed Argonne National Laboratory (JCESR managing partner) by S. Ha and K. G. Gallagher, Journal of Power Sources, Volume 296, pp 122–132.

