Scientific Achievement
This part I review serves as a self-contained article that addresses the fundamentals of batteries and cathode degradation mechanisms.
Significance and Impact
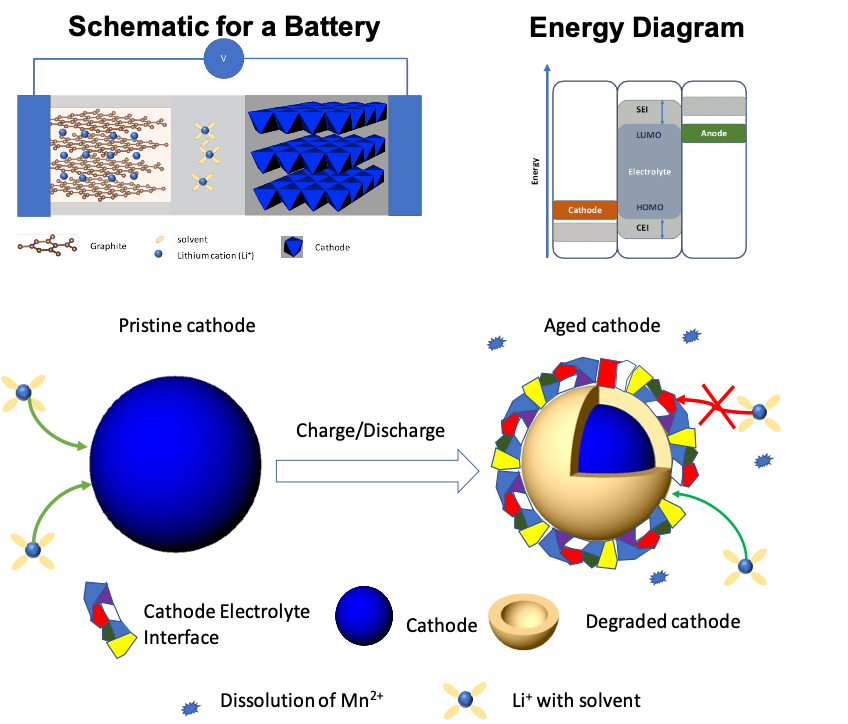
we outline the basics of batteries and explain the common cathode degradation mechanisms. The goal is to understand the connection of battery performance with electrolytes and additives, and the role of interfaces formed from interactions of electrolytes/additives at the electrode surfaces.
Research Details
- Introduction to Batteries of Lithium Ion Batteries and Next Generation Li Ion Batteries
- Capacity Fading Mechanisms of Cathode Materials:
- 1. Lithium Cobalt Oxides (LiCoO2, LCO)
- 2. Ternary Cathode Materials: Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxides (LiNixMnyCozO2,x+y+z=1, NMC) and Lithium Manganese Rich-NMC (xLi2MnO3•(1−x)LiMO2 (M = Ni, Co, Mn), LMR-NMC)s
- 3. Spinel Cathodes (Lithium Manganese Oxides, LiMnO2, and Lithium Nickel Manganese Oxides, LiNi0.5Mn1.5O2) and Olivine Cathodes
- 4. (Lithium Transition-Metal Phosphate, LiMPO4)

