Scientific Achievement
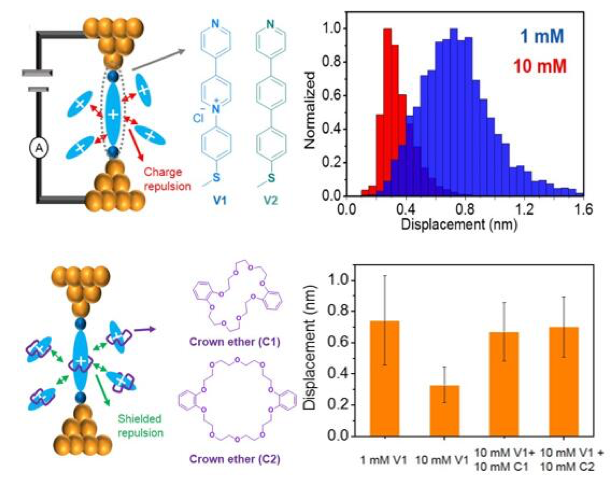
Our results show that charge transport in redox-active pyridinium-based molecules can be modulated by host-guest interactions and intermolecular electrostatic effects.
Significance and Impact
This work highlights the use of single molecule techniques to characterize the effects of intermolecular interactions on charge transport, which may aid in the design of new electrolytes for redox-active flow batteries with tunable electronic properties.
Research Details
- Pyridinium-based molecules exhibit charge transport over reduced molecular displacements upon increasing the solution concentration of the charged pyridinium complex, which is attributed to intermolecular electrostatic effects.
- Formation of host-guest complexes via addition of a crown ether resulted in recovery of charge transport over molecular displacements corresponding to single pyridinium junctions at low concentrations, thereby suggesting that host-guest complexes efficiently screen electrostatic repulsions between cationic molecules.

