Scientific Achievement
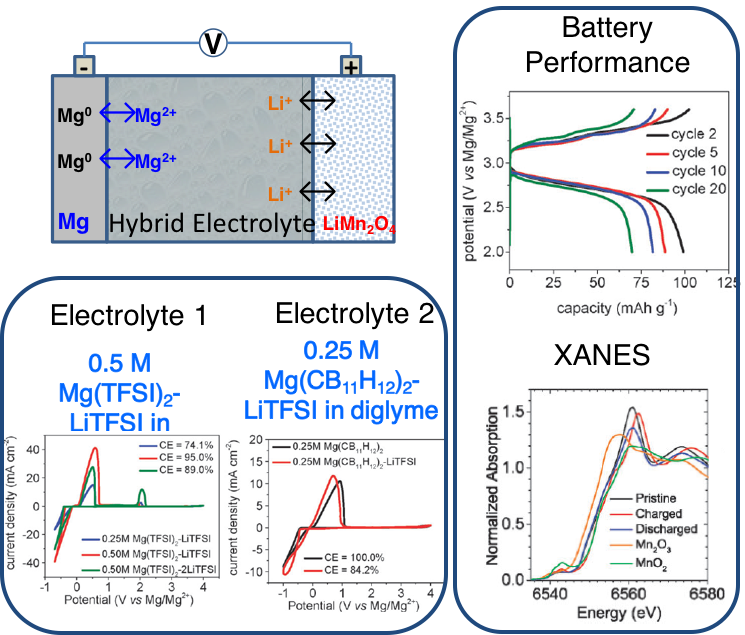
Two Mg-Li dual salt hybrid electrolytes were developed with excellent oxidative stability up to around 3.8 V (vs Mg/Mg2+) on a aluminum current collector, enabling the successful coupling of several state-of-the-art lithium-ion intercalation cathodes (LiMn2O4, LiCoO2 and LiNi1/3Mn1/3Co1/3O2) with magnesium metal anodes.
Significance and Impact
The Mg-LiMn2O4 battery delivers about 106 mAh g-1 initial discharge capacity with the working voltage of around 2.8 V (vs Mg/Mg2+), highlighting the highest working voltage rechargeable batteries with magnesium metal anodes to date.
Research Details
- Mg(TFSI)2–LiTFSI/diglyme and Mg(CB11H12)2–LiTFSI/tetraglyme are proven to plate/strip Mg with a high coulombic efficiency and are efficient dual salt electrolytes for high voltage hybrid batteries with magnesium metal anodes
- Both electrolytes enable the lithium ion intercalation in the hybrid batteries with high voltage LMO as the cathode and magnesium metal as the anode
Work performed at Argonne National Laboratory (JCESR managing partner) by B. Pan, Z. Feng, N. Sa, S.-D. Han, Q. Ma, P. Fenter, J. Vaughey, Z. Zhang, and C. Liao, Chemical Communications 2016

