Scientific Achievement
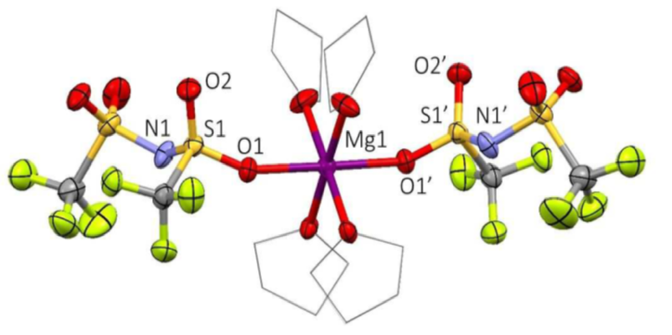
Electrolytes for Mg-ion batteries are a complex mixture of salts, solvents, and additives that allow for the free-movement of Mg-ions across the cell. By addition of simple amines to the mixture, the internal equilibriums are shifted to allow formation of a simpler neutral complex in solution that does not require use of corrosive halide anions (Figure 1).
Significance and Impact
A family of electrolyte additives has been identified that alter the complex anion equilibrium solution. In-situ NMR studies indicate that while the DMA is not incorporated into the isolated species, it is incorporated in the transient complexes seen in solution and appears directly bonded to the Mg-ion while in solution increasing the solubility of the Mg(TFSI)2.
Research Details
- Single crystal analysis shows that a neutral Mg(TFSI)2(THF)4 species is in equilibrium in solution that is soluble in protic but aprotic ethers.
- Combined PDF and NMR analysis of the DMA addition to the electrolyte shows that the molecule binds in a transient fashion to shift the solution equilibria to a simpler species.

