Scientific Achievement
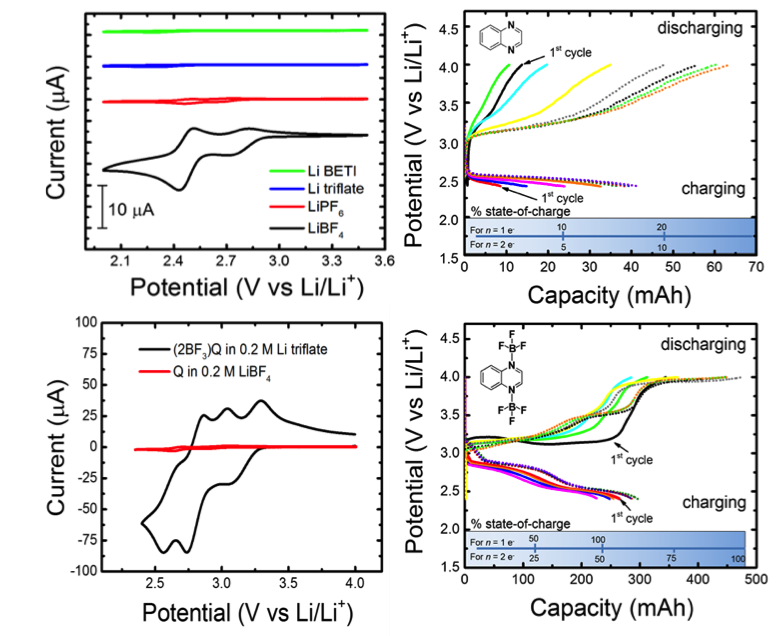
Quinoxalines are highly sensitive to solvent and electrolyte interactions. For example, bare quinoxaline is active in acetonitrile at DFT-predicted potentials but is effectively dead in propylene carbonate. Electrochemical activation is achieved by addition of BF3-ligands.
Significance and Impact
Electrolyte choice shown to strongly dictate the mechanism and cycling stability, either through direct interactions with the active species, or a solution or surface mediated process
Research Details
- Empirical and DFT results show quinoxaline becomes electrochemically active upon forming adducts with BF3, a lewis acid present in solution due to decomposition of electrolyte via interactions with trace water and thermolysis
- We synthesized the DFT-predicted molecule, 2(BF3)quinoxaline, which showed enhanced electrochemical activity and capacity compared to previous tests of bare quinoxaline
Work performed at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (JCESR collaborator), Argonne National Laboratory (JCESR managing partner) and University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (JCESR partner) E.V. Carino, C.E. Diesendruck, J.S. Moore, L.A. Curtiss, R.S. Assary, F.R. Brushett. RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 18822-18831.
DOI: 10.1039/C5RA00137D

