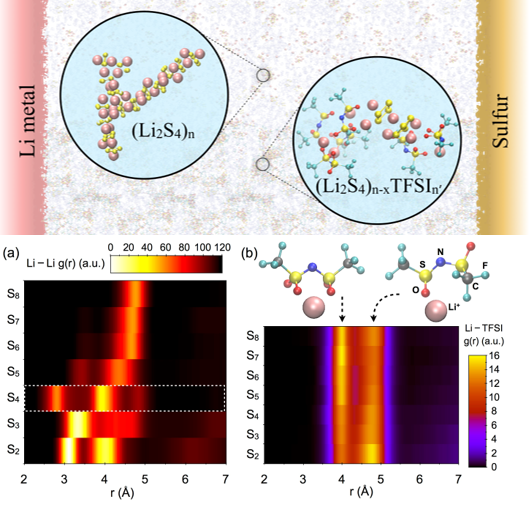
Lower panel: Radial distribution function of (a) Li-Li in Li2Sx (x= 2 to 8) and Li-TFSI in Li2Sx (x= 2 to 8) + Li(TFSI) in DOL:DME solvent
Scientific Achievement
A coupled theoretical and experimental study of bulk solvation structure and transport properties of lithium salt (Li-TFSI) and polysulfides species revealed extensive cluster formation in lower order polysulfides (Sx2-; x≤4), whereas the longer polysulfides (Sx2-; x>4) show high solubility and slow dynamics in the solution.
Significance and Impact
Optimal solvent/salt ratio is essential to control the solubility and conductivity as the addition of lithium salt increases the solubility but decreases the mobility of the ionic species.
Research Details
- Simulations and NMR results show large cluster formation in lower order polysulfides, while higher solubility is observed with an increase in polysulfide chain length
- The addition of salt (Li-TFSI) weakens the strong Li+-Sx2- networks due to competing interactions between TFSI- and polysulfide di-anions with Li+.
- A high salt concentration reduces the mobility of ionic species, which may negatively impact the ionic conductivity of the electrolyte.
Work performed at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (JCESR partner), Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (JCESR partner) and Argonne National Laboratory (JCESR managing partner) by Rajput, N. N.; Murugesan, V.; Shin, Y.; Han, K. S.; Lau, K. C.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Curtiss, L. A.; Mueller, K. T.; Persson, K. A, Chem. Mater. 2017.

