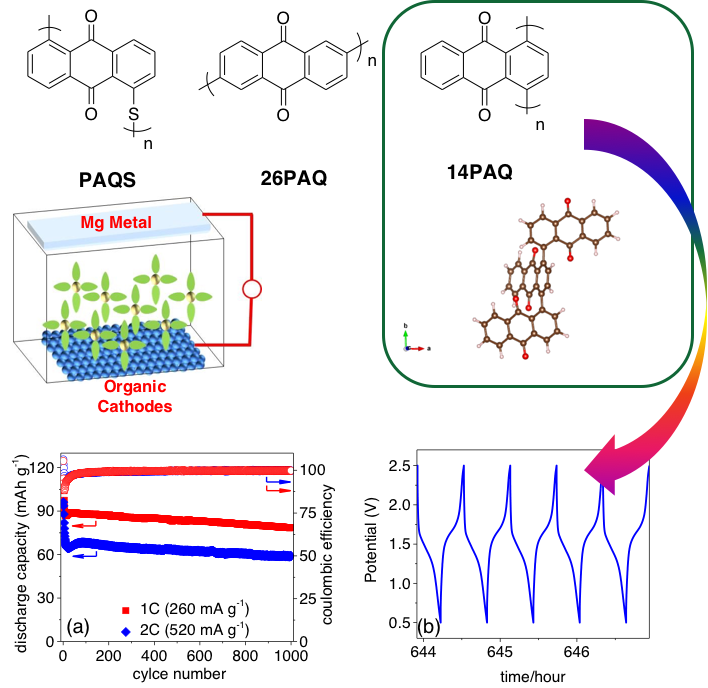
Scientific Achievement
A series of anthraquinonyl-based polymers (PAQS, 14PAQ, and 26PAQ) have been prepared and evaluated as high-performance organic cathodes for rechargeable Mg-ion batteries. Mg-14PAQ system shows the best cycling stability among the series: at the current rate of 0.5C, 104.9 mAh g-1 discharge capacity can be obtained in the 100th cycle; successful 1000 cycles with a small amount of capacity loss at 1C.
Significance and Impact
Instead of using a Mg electrolyte containing corrosive and toxic strong Lewis acid AlCl3, environmentally benign non-nucleophilic Mg(HMDS)2-4MgCl2 (HMDS = hexamethyldisilazide) in THF solution was chosen as the electrolyte with high compatibility toward the electrodes. The success of organic polymer electrodes for Mg ion batteries opens a new door to the development of high voltage, high capacity Mg ion batteries.
Research Details
- Two anthraquinone-based polymers, 26PAQ and 14PAQ, aiming at improving the capacity retention for advanced magnesium ion batteries, were synthesized according to the modified literature procedures. The excellent battery cycling performance was demonstrated with Argonne patented electrolyte (Mg(HMDS)2-4MgCl2).
Work performed at Argonne National Laboratory (JCESR managing partner) by B. Pan, J. Huang, Z. Feng, L. Zeng, M. He, L. Zhang, J. Vaughey, M. Bedzyk, P. Fenter, Z. Zhang, A. Burrell, and C. Liao, Advanced Energy Materials

