Scientific Achievement
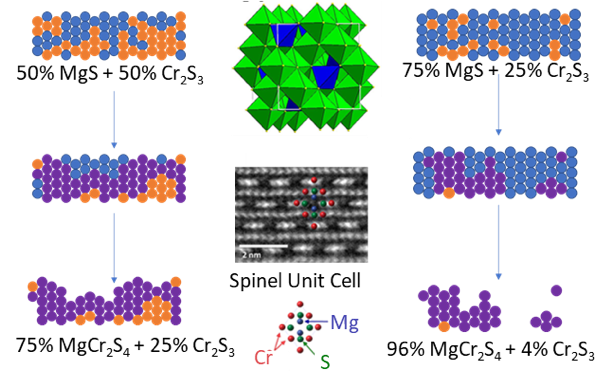
MgCr2S4 was synthesized for the first time. This thiospinel material is predicted to have a high insertion voltage relative to the isostructural MgTi2S4 studied by the center. This synthesis serves as a starting point for making other unknown battery materials.
Significance and Impact
This synthesis allows empirical validation of theoretical predictions made at Berkeley Lab. Thiospinels are predicted to have high magnesium mobility and have been studied as both cathodes and solid state electrolytes. However, the relatively low number of magnesium thiospinels has limited this research.
Research Details
- MgCr2S4 was synthesized from the elements. The reaction rate was increased by adding an excess of MgS to the starting mixture.
- This material was characterized using NMR (ANL+PNNL), electron microscopy (UIC) and electrochemical techniques (ANL) by a team of JCESR experts.

