Scientific Achievement
2,5-dimethoxyl-1,4-benzoquinone (DMBQ) was investigated as 2 V (vs Mg/Mg2+) organic cathode material for non-aqueous rechargeable magnesium-ion batteries
Significance and Impact
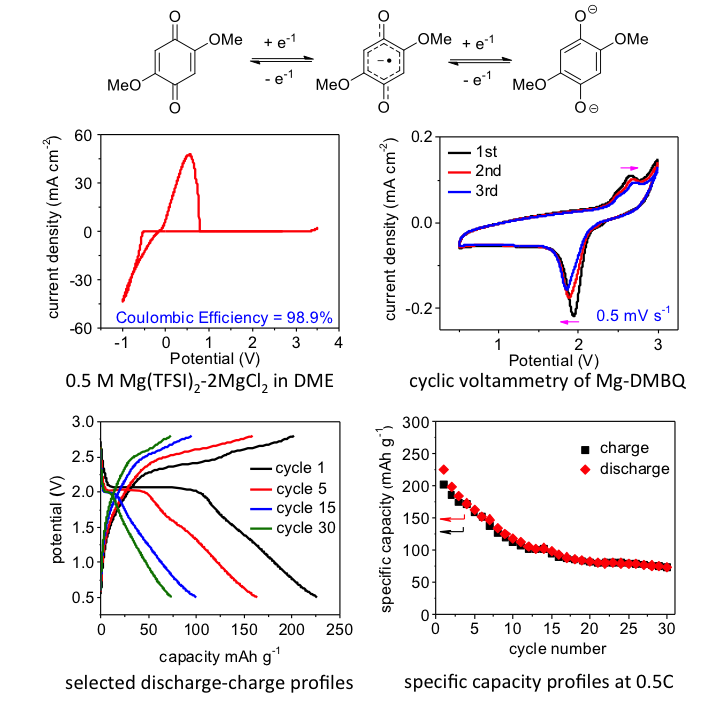
Mg-DMBQ batteries were demonstrated to work with a discharge voltage above 2 V (vs Mg/Mg2+), which is superior to the previous reported potential in Mg-DMBQ batteries with conventional magnesium salt-based electrolytes (< 1.1 V, vs Mg/Mg2+), and also excels the well-known Chevrel phase Mo6S8 in magnesium-ion batteries (1.2 V, vs Mg/Mg2+)
Research Details
- The reversibility of DMBQ as cathode material in Mg-ion batteries was demonstrated in the cyclic voltammogram measurement with the observation of the redox potential at about 2.3 V (vs Mg/Mg2+)
- The Mg-DMBQ battery was proven capable of delivering above 200 mAh g-1 initial specific capacity with the discharge plateau above 2 V (vs Mg/Mg2+)
- The reversibility of DMBQ in magnesium ion batteries was further demonstrated by the ex situ XRD measurement, and the influence of the electrolyte on the battery performance was also extensively investigated
Work performed at Argonne National Laboratory (JCESR managing partner) by B. Pan, D. Zhou, J. Huang, L. Zhang, A. K. Burrell, J. T. Vaughey, Z. Zhang, and C. Liao, Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2016, 163 (3), A580-A583.
DOI: 10.1149/2.0021605jes

